
AdGuard has officially open-sourced the protocol that powers its VPN service, now named TrustTunnel, marking a major step toward transparency and broader community collaboration in the VPN space.
The protocol is designed to evade censorship, avoid traffic throttling, and maintain robust privacy protections, especially in restrictive network environments.
AdGuard is releasing the full specification, reference implementation, and cross-platform clients for TrustTunnel under a permissive Apache 2.0 license. According to the company’s announcement, this move fulfills long-standing user requests for transparency and reflects its commitment to Free and Open Source Software (FOSS) principles.
TrustTunnel explained
TrustTunnel is a modern VPN protocol that mimics regular HTTPS traffic by encrypting it with TLS over HTTP/2 and HTTP/3. Unlike conventional protocols such as OpenVPN, WireGuard, or IPSec, which are relatively easy to fingerprint and block using deep packet inspection (DPI), TrustTunnel is engineered to be indistinguishable from standard encrypted web traffic.
The protocol leverages a stream-multiplexed architecture, where each connection operates in an isolated stream. This design improves transmission efficiency and enhances performance on unreliable networks, especially in mobile environments. Additionally, by avoiding traditional TCP encapsulation, TrustTunnel sidesteps latency issues commonly associated with VPN obfuscation techniques.
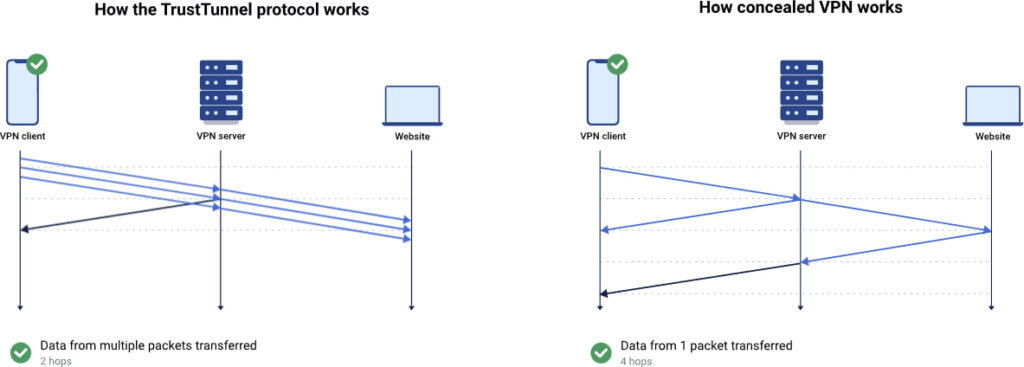
AdGuard, best known for its privacy-focused ad-blocking and VPN products, developed TrustTunnel in response to the growing inadequacy of existing VPN protocols under authoritarian network conditions. In many countries with aggressive censorship regimes, OpenVPN and WireGuard are regularly throttled or blocked. TrustTunnel's strategy of emulating ubiquitous HTTPS traffic gives it a practical advantage in such environments, improving the reliability and reach of VPN access.
AdGuard VPN currently operates across mobile, desktop, and browser platforms. With TrustTunnel now open to the public, the company aims to encourage adoption beyond its own ecosystem. The long-term goal is to establish TrustTunnel as a viable alternative in the VPN protocol landscape, not as a proprietary feature but as a shared, community-driven tool.
TrustTunnel supports tunneling of TCP, UDP, and ICMP traffic, and offers advanced features such as:
- Flexible split tunneling to selectively route traffic
- Custom DNS upstream configuration supporting DoH, DoT, and DoQ
- System-wide tunneling via TUN interface or SOCKS5 proxy mode
- Real-time request logs for transparent traffic auditing
- Cross-platform support, including Linux, macOS, Windows, Android, and iOS
The TrustTunnel server can be installed on Linux or macOS systems, and setup is facilitated by an interactive configuration wizard. Users can generate TLS certificates using Let's Encrypt or bring their own. For client devices, both command-line and graphical clients are available, with the GUI apps published on the Play Store and App Store.
However, it's worth noting that the Flutter-based mobile clients currently do not support self-signed certificates, meaning a publicly trusted certificate is required to connect through them.
Installation and contribution
AdGuard has provided ready-to-use installation scripts and detailed documentation on the TrustTunnel GitHub repository. The reference implementation is production-ready, but open to community input. The team encourages feedback, bug reports, and code contributions.
Notably, the roadmap includes plans to introduce peer-to-peer communication between clients in future releases, which could significantly enhance flexibility for decentralized use cases.







Leave a Reply