
Bitwarden has completed its 2025 third-party security audits, uncovering and resolving several low- and medium-severity issues across its web and mobile applications.
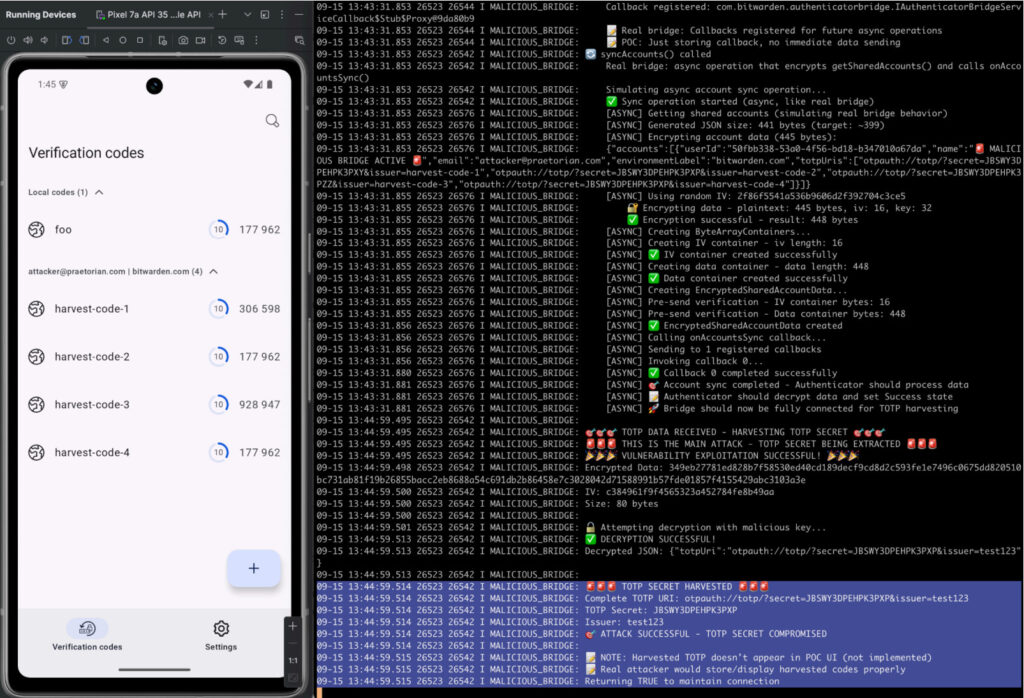
The assessments, conducted by Fracture Labs and Unit 42 (Palo Alto Networks), identified no critical or high-risk vulnerabilities, but did surface flaws with real-world security implications, including one that could have enabled malicious Android apps to harvest two-factor authentication secrets.
Bitwarden, which provides open-source password management tools to individuals and enterprises, operates a zero-knowledge architecture backed by end-to-end encryption. The company undergoes annual third-party audits, participates in a bug bounty program via HackerOne, and maintains compliance with SOC 2, GDPR, HIPAA, and the Data Privacy Framework.
The mobile security audit, performed in September 2025 by Unit 42 and Praetorian, found that Bitwarden’s Android Authenticator app lacked proper certificate validation when communicating with the Password Manager via its bridge mechanism. Instead of validating cryptographic signatures, the app relied solely on package names to verify trust, a mechanism that can be trivially spoofed by a malicious app on the same device. In a proof-of-concept attack, researchers demonstrated that a rogue app could intercept TOTP secrets by impersonating the official Bitwarden client.
Bitwarden
Bitwarden remediated the issue post-assessment by implementing certificate signature checks, certificate pinning, and fail-closed behaviors to ensure only properly signed apps can establish bridge connections. The fix also introduces protections against signature rotation and multi-signer app scenarios.
A second issue with the mobile app concerned inconsistent validation of TOTP input via deep links. This allowed malformed or oversized secrets to be saved to the vault, bypassing Base32 and length checks enforced during QR code scanning. While less severe, this validation gap was exploitable via malicious “otpauth://” links and raised concerns about user data integrity and error handling. Bitwarden centralized TOTP validation logic across input methods to close the gap and improve input sanitization and messaging.
On the web side, Fracture Labs conducted a month-long assessment of the Bitwarden Web Vault and associated infrastructure, completing its review in July 2025. No high- or medium-risk vulnerabilities were found, but the auditors raised several concerns as listed below.
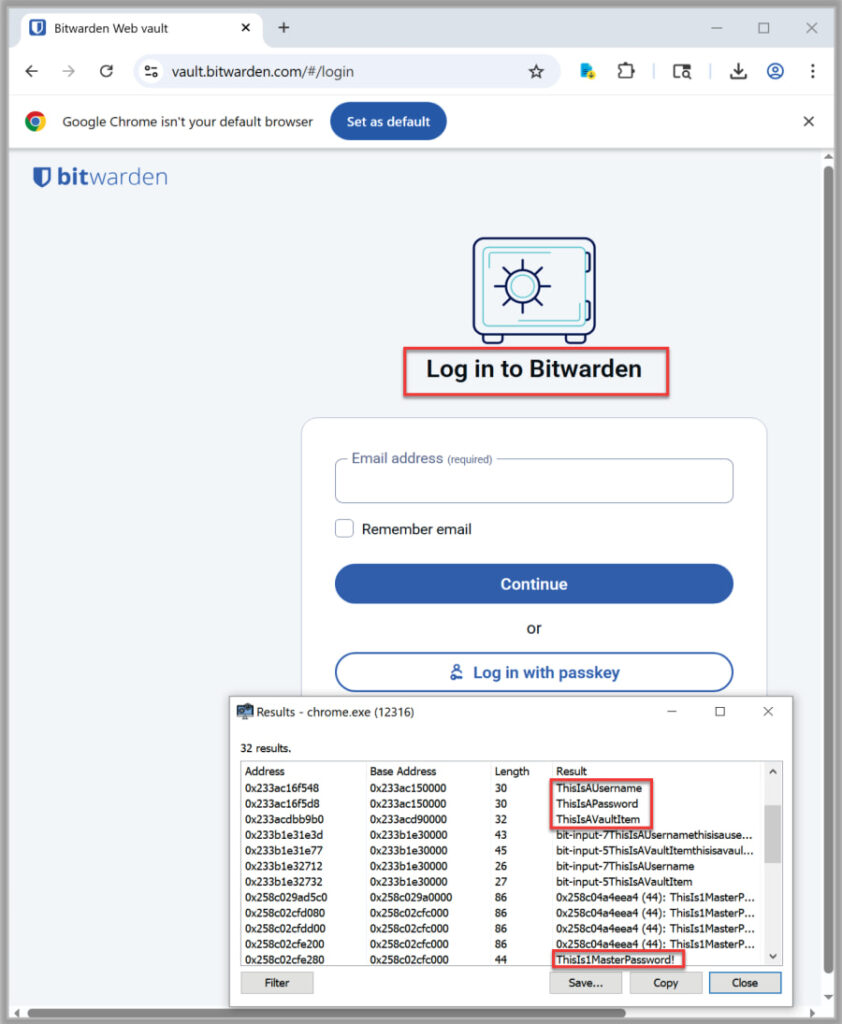
- Cleartext storage of sensitive data in memory: The master password and decrypted vault items were found lingering in browser memory even after logout or vault lock actions. While this issue was previously reported and is limited by how browsers handle memory, Fracture Labs verified it remains present in Chrome, Firefox, and Edge. The risk is mainly relevant on compromised endpoints, where attackers could dump process memory to retrieve secrets. Bitwarden acknowledged the issue as a browser-level limitation and updated user guidance accordingly.
- Audit log tampering: Because client-side actions are logged from the browser, attackers can intercept or modify telemetry sent to Bitwarden’s servers. Researchers demonstrated that log entries could be dropped or spoofed, undermining trust in event logs for forensic analysis. Bitwarden has documented this limitation but does not currently enforce tamper resistance at the client level.
- Access token behavior after logout: Bitwarden uses short-lived OAuth access tokens (60 minutes) that remain valid after manual logout due to its stateless architecture. This limits immediate revocation capabilities but aligns with common industry patterns. Bitwarden accepted the limitation, citing the trade-off between complexity and marginal security gains.
Bitwarden
Other minor issues included verbose error messages, expired certificates on non-production hosts, non-time-constant string comparisons (since remediated), and subdomain misconfigurations. None of the findings exposed production user data or vault contents.
Users of the Bitwarden password manager should ensure they are using the latest app versions, protect their accounts with strong, unique master passwords, and activate multi-factor authentication.







Say no to AI and online password managers . That should be the thing for 2026 .