
Microsoft has shared new details and assurances regarding the security and privacy architecture of its Recall feature, designed for Copilot+ PCs.
The feature aims to help users easily find content they've previously seen on their PCs, offering a seamless experience in managing on-screen content. However, due to its powerful capabilities, Recall has faced scrutiny over potential security risks.
Recall was met with concerns earlier in its development, particularly around the risk of local data storage and exposure of sensitive information. Security researcher Kevin Beaumont highlighted risks associated with local storage decryption, ease of data extraction, lack of user control, and the potential for sensitive data exposure. Microsoft's opt-in design, enhanced user controls, and encryption-focused security measures were introduced as a direct response to this criticism, aiming to prevent unauthorized data access and large-scale breaches.
Recall's design principles
According to David Weston, Vice President of Enterprise and OS Security at Microsoft, Recall is being developed with four core principles to safeguard user data:
User Control: Recall is an fully opt-in feature. Users must actively enable it during the Copilot+ setup process, and it remains off by default. Furthermore, users have full control over deleting, pausing, or turning off Recall at any point.
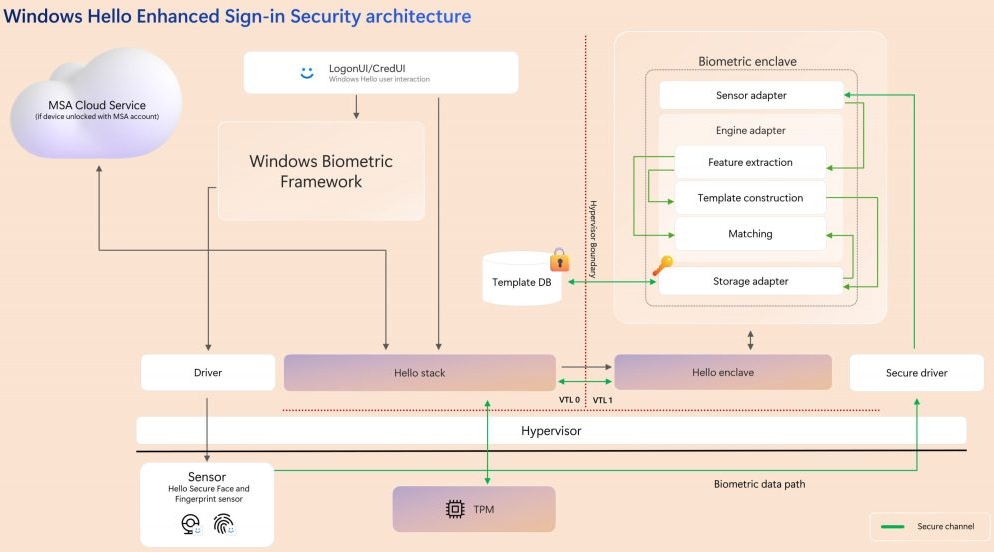
Encryption and Key Protection: Snapshots saved by Recall, which represent what is displayed on-screen, are encrypted, and their decryption keys are protected within a Trusted Platform Module (TPM). Additionally, operations involving these keys occur within a secure Virtualization-based Security Enclave (VBS Enclave), preventing unauthorized access.
Service Isolation: The operations that process and decrypt snapshot data are isolated within the VBS Enclave. This isolation prevents unauthorized code or users from accessing sensitive information stored within Recall.
User Intent and Authorization: User actions in Recall, such as changing settings or accessing the user interface, require explicit authorization through Windows Hello Enhanced Sign-in Security (ESS). ESS includes biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, adding an additional layer of security.
Microsoft
Enhanced security architecture
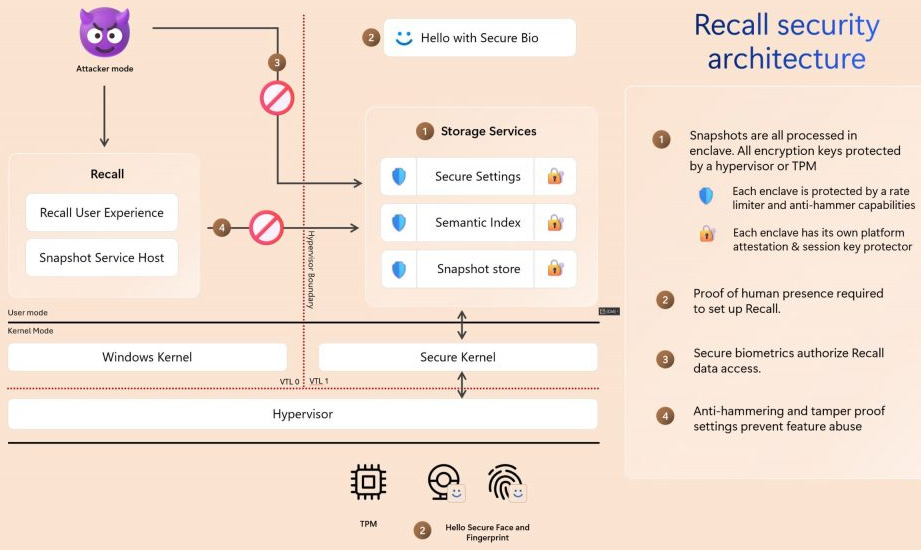
Recall leverages the power of VBS Enclaves, which use the same hypervisor technology as Azure, to create isolated secure areas within the system's memory. This architecture follows Zero Trust principles, meaning that the environment must be securely attested before sensitive operations like snapshot processing are performed.
Snapshots and their associated data are only accessible after users authenticate using their Windows Hello credentials. This protection is not just against unauthorized access but also malware attempts to exploit Recall data, which is safeguarded through features like rate-limiting and anti-hammering mechanisms.
Recall's secure architecture is based on several key components, including:
- Security configurations for Recall are stored in a protected data store within the VBS Enclave. Any attempt to change these settings requires user authorization.
- To allow users to search through snapshots effectively, Recall converts content into vectors, which are encrypted and stored within the VBS Enclave. All search and query operations are performed securely within this enclave.
- Snapshots and metadata, such as timestamps and app details, are stored locally on the device and encrypted individually. The encryption keys are protected by the VBS Enclave.
- The user interface for searching and viewing snapshots operates outside the secure enclave, while the snapshot service is responsible for saving, querying, and processing data securely.
Microsoft
In-depth auditing
Microsoft says it has conducted extensive security reviews to validate Recall's security against various exploitation scenarios. The most important of those are highlighted as follows.
- The Microsoft Offensive Research & Security Engineering (MORSE) team performed design reviews and penetration testing over several months.
- An independent security vendor conducted a security review and penetration test to evaluate Recall's architecture.
- Recall underwent a Responsible AI Impact Assessment to address potential risks, harms, and mitigation strategies aligned with Microsoft's principles of fairness, privacy, and security.
Finally, it's important to note that only Copilot+ PCs that meet the “Secured-core” standard can utilize Recall, so if your computer doesn't belong to this category, the feature won't be available to you. These devices come equipped with advanced security measures such as BitLocker encryption, TPM 2.0 for hardware-rooted security, Virtualization-based Security (VBS), Kernel DMA Protection, and dynamic root-of-trust measures like Measured Boot and System Guard Secure Launch.







Leave a Reply