
The Ukrainian government's cybersecurity team, CERT-UA, discovered an alarming cyber-sabotage campaign by the Sandworm group, also known as UAC-0133 or APT44, targeting nearly twenty critical infrastructure sites across Ukraine.
This extensive operation aimed to disrupt the operational integrity of the nation's energy, water, and heating sectors, leveraging sophisticated malware tools and supply chain vulnerabilities.
Analysis of the APT44 attack
CERT-UA's rapid response revealed a coordinated effort to compromise information and communication systems (ICS) in ten regions. The discovery included previously recognized malware from 2022, such as QUEUESEED (known variants: KNUCKLETOUCH, ICYWELL, WRONGSENS, KAPEKA), and the introduction of new malware like LOADGRIP and BIASBOAT. These malicious tools were specifically tailored to target systems running on Linux and deployed to manage automated process control systems using domestically produced software-defined radios (SDR).
The new malware BIASBOAT, camouflaged as an encrypted file server, was one of the tools used to infiltrate enterprise systems. This breach was facilitated partly through the exploitation of supply chain weaknesses, where initial unauthorized access was linked to compromised SDRs embedded with software bookmarks and vulnerabilities, possibly during routine technical support by supplier employees.
During the period from March 7 to March 15, 2024, CERT-UA undertook extensive measures to notify affected enterprises and mitigate the threats. Their efforts included the establishment of incident chronologies, malware removal, and the reinforcement of server and network equipment security.
Notably, on Windows OS systems, APT44 deployed QUEUESEED alongside another malware, GOSSIPFLOW, previously observed in attacks on water facilities and characterized by its use of the SDELETE method.
CERT-UA
Overview of deployed malware
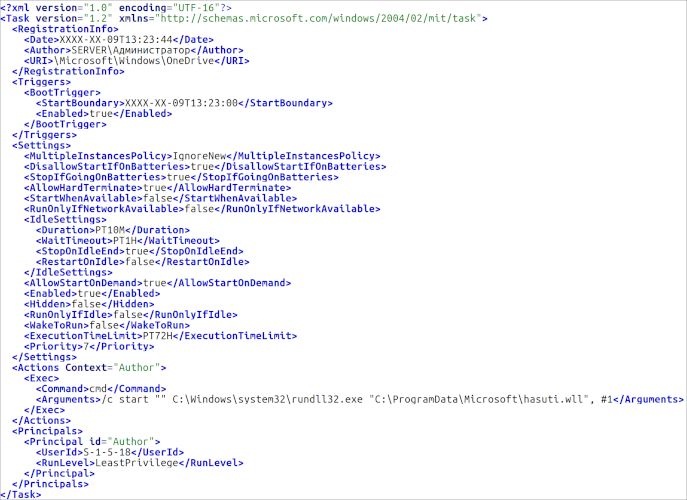
- QUEUESEED: Developed in C++, this malware gathers basic system info and executes commands received from a control server, transmitting data encrypted via RSA+AES. Its persistence on infected machines is maintained through registry modifications or scheduled tasks.
- BIASBOAT: A Linux variant of QUEUESEED, executed with the aid of the LOADGRIP injector, which is itself a payload execution tool utilizing ptrace API for injection of encrypted payloads (AES128-CBC).
- GOSSIPFLOW: Written in Go, this malware constructs tunnels using the Yamux library and provides SOCKS5 proxy functionality, aiding in the concealment and management of network traffic during the attacks.
CERT-UA also highlighted the use of other hacking tools by APT44 such as CHISEL, LIBPROCESSHIDER, and variants of the notorious JUICYPOTATONG and ROTTENPOTATONG, enhancing the attackers' capabilities to evade detection and maintain control over compromised systems.
This incident underscores the need for robust cybersecurity defenses in critical infrastructure sectors. Enterprises are advised to improve server segmentation, rigorously analyze software provided by suppliers for vulnerabilities, and enhance overall security protocols to prevent similar large-scale cyberattacks. Organizations should also prioritize rapid detection and response strategies to mitigate potential threats effectively.







Leave a Reply