
ESET researchers have detailed a sophisticated exploitation campaign by the Russia-aligned hacking group RomCom, which utilized two newly discovered zero-day vulnerabilities. The flaws, CVE-2024-9680 in Mozilla Firefox and CVE-2024-49039 in Microsoft Windows were chained together to enable highly effective, user-interaction-free attacks targeting victims globally.
RomCom, also known as Storm-0978, has gained notoriety for combining cyber-espionage and financial cybercrime. The group, previously linked to Microsoft Word exploits, targets a wide array of sectors, including government, defense, and energy, focusing heavily on Ukraine. The RomCom backdoor is capable of executing commands, stealing credentials, and downloading additional malicious modules.
ESET
Exploit breakdown
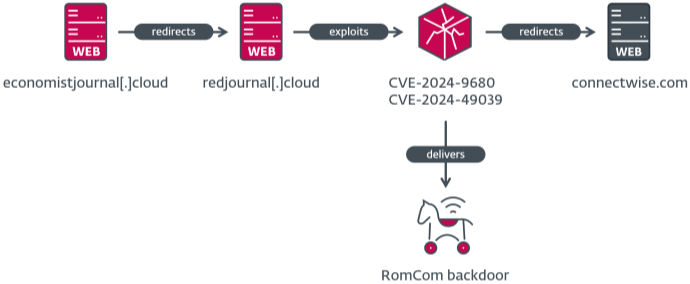
The campaign began with the exploitation of CVE-2024-9680, a critical use-after-free vulnerability in Firefox's animation timeline subsystem. Once triggered via a crafted web page, the vulnerability allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code within Firefox's sandbox. However, the attackers went a step further by leveraging CVE-2024-49039, a Windows privilege escalation bug, to escape the sandbox and gain higher-level system access. The culmination of this attack chain was the installation of RomCom's proprietary backdoor, a powerful malware used for espionage and cybercrime.
ESET
The compromise chain involved luring victims to malicious websites designed to exploit the Firefox vulnerability. Once successful, shellcode was executed, downloading and installing the RomCom backdoor. A second-stage payload leveraged the Windows Task Scheduler exploit to escape Firefox's restrictions. Notably, this attack required no user interaction — users simply needed to visit a compromised website using vulnerable Firefox or Tor Browser versions.
Key tools identified in the attack included:
- JavaScript exploits (e.g., main-128.js for Firefox versions 106–128 and main-tor.js for Tor Browser 12 and 13).
- A Reflective DLL Injection (RDI) implementation to load malicious DLLs bypassing sandbox restrictions.
- Fake domains mimicking legitimate services (e.g., redircorrectiv[.]com) and command-and-control (C&C) servers.
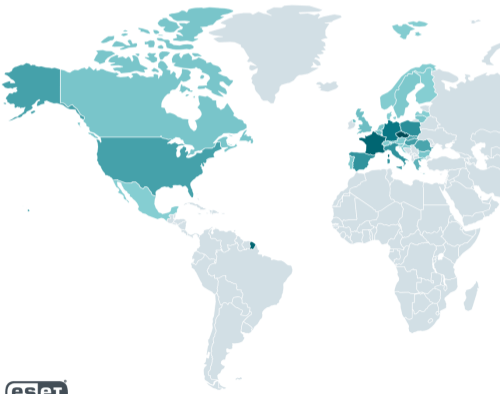
According to ESET telemetry, the campaign spanned Europe and North America, with hundreds of potential victims ranging from government entities to businesses.
Patches and mitigations
ESET reported CVE-2024-9680 to Mozilla on October 8, 2024. Mozilla swiftly patched the vulnerability within 24 hours, releasing updates for Firefox, Firefox ESR, Tor Browser, and Thunderbird. Microsoft released its patch for CVE-2024-49039 a month later, on November 12, 2024, closing the privilege escalation loophole.
To defend against RomCom exploits, users should update to Firefox 131.0.2 and later, and Tor 13.5.7 and later, apply the latest Windows security update, and enable security features on the browser to limit JavaScript execution and sandbox escapes.







Leave a Reply