
SafeBreach Labs released a proof-of-concept (PoC) exploit for CVE-2024-49113, a Denial-of-Service (DoS) vulnerability in the Microsoft Windows Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP). Alongside this, researchers detailed their attempts to exploit the related CVE-2024-49112, a Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability, emphasizing its potential for severe impact.
These vulnerabilities affect Microsoft Windows and Windows Server platforms and were addressed in the December 2024 security updates. NHS England's National Cyber Security Operations Centre (CSOC) has classified the likelihood of exploitation as high, urging organizations to act swiftly.
Vulnerability breakdown
CVE-2024-49113 is classified as a Denial-of-Service (DoS) issue, and has a CVSS score of 7.5. It allows unauthenticated remote attackers to send malicious LDAP requests that crash Windows Server systems, disrupting operations and requiring a reboot to restore functionality. While its immediate impact is limited to service downtime, the potential for widespread disruption in enterprise environments makes it a critical concern.
On the other hand, CVE-2024-49112 is a more severe Remote Code Execution (RCE) vulnerability with a CVSS score of 9.8. It enables attackers to craft malicious LDAP calls that execute arbitrary code, granting them control over the LDAP service. Since LDAP is integral to directory-based authentication and system management, successful exploitation of this flaw could result in full system compromise.
Both vulnerabilities were patched in Microsoft's December 2024 security update, but the release of the CVE-2024-49113 PoC highlights the urgency for organizations to apply the updates if they haven't done so already.
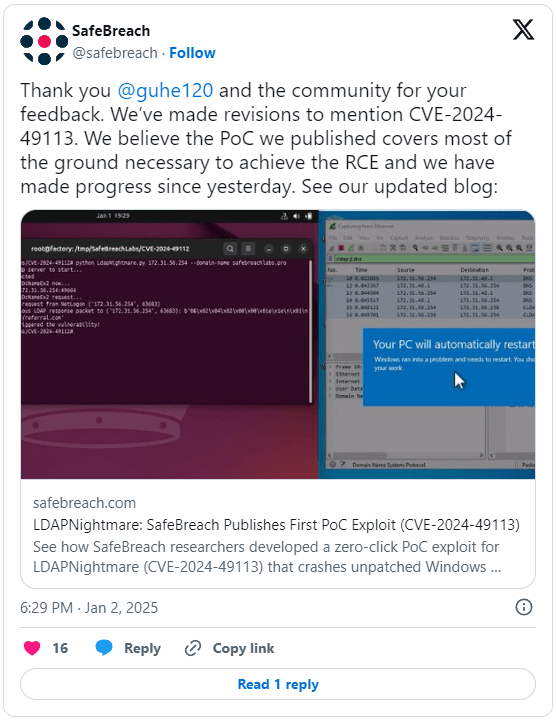
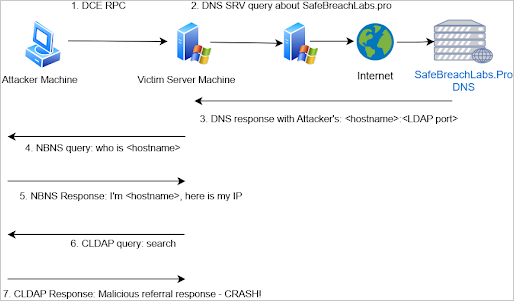
SafeBreach's exploitation method
The PoC for CVE-2024-49113, dubbed LDAP Nightmare, demonstrates the vulnerability's exploitation mechanics:
- An asynchronous LDAP server is configured to listen for connections.
- Using the Netlogon Remote Protocol (NRPC), the victim server is coerced into sending an LDAP query to the attacker-controlled server.
- A specially crafted response from the attacker’s server exploits the vulnerability, crashing the target system.
The attempt to create a PoC for CVE-2024-49112 remains incomplete but includes detailed insights into the exploitation approach. According to the SafeBreach blog, the RCE flaw could be weaponized using similar LDAP interaction techniques, posing a significant risk to unpatched systems.
SafeBreach
Microsoft's response
Both vulnerabilities were included in Microsoft's December 2024 Patch Tuesday updates, which addressed 72 vulnerabilities, including CVE-2024-49112 and CVE-2024-49113. The patch for these vulnerabilities was part of the cumulative update KB5048685, targeting Windows 11 versions 22H2 and 23H2, and Windows Server variants.
The December update was a critical release due to the inclusion of fixes for actively exploited vulnerabilities like CVE-2024-49138, a zero-day flaw in the Windows Common Log File System.
To mitigate risks from these vulnerabilities, affected organizations should ensure Microsoft's December 2024 updates are installed, limit LDAP server access to trusted systems, and enforce strict access control measures. If LDAP is not required, disable it on vulnerable servers.







Leave a Reply