
A new Mac stealer named “Poseidon” is being distributed via malicious Google ads targeting people looking to download the popular Arc browser, according to a report by Malwarebytes. The stealer, developed by a cybercriminal known as Rodrigo4, is designed to exfiltrate sensitive information from infected devices and is actively being promoted on underground forums.
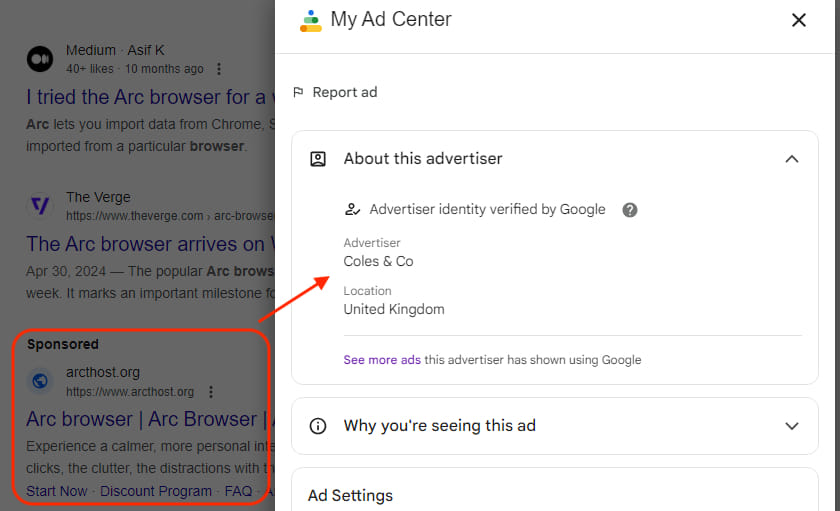
On June 24, 2024, Malwarebytes researchers observed the new campaign distributing Poseidon through deceptive Google ads. The ads, which masqueraded as legitimate promotions for the Arc browser, redirected users to a fraudulent site offering a malicious DMG installer.
This method of distribution indicates the stealer's development and its targeted approach towards Mac users, leveraging the increasing popularity of the Arc browser.
Malwarebytes
Poseidon is a rebranded and updated version of OSX.RodStealer, a malware previously tracked by Malwarebytes. The new stealer incorporates additional features such as the ability to steal VPN configurations from Fortinet and OpenVPN. Despite these enhancements, a significant portion of its codebase remains identical to its predecessor, Atomic Stealer (AMOS), known for its capabilities in data exfiltration.
Malwarebytes
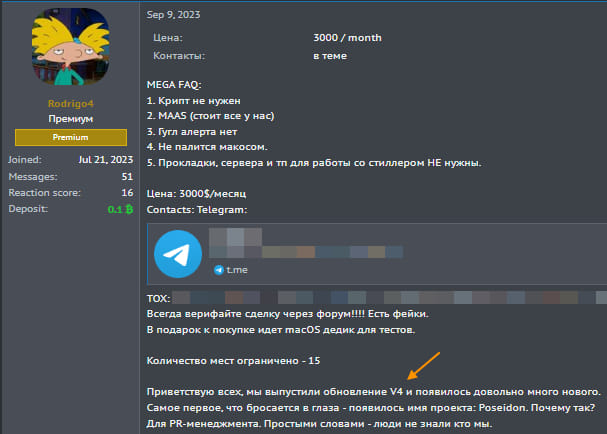
Rodrigo4, a threat actor active on the XSS underground forum, announced the rebranding of his project to Poseidon on June 23. The announcement highlighted several new features aimed at attracting buyers in the cybercrime community. The stealer includes functionalities such as:
- File grabber
- Crypto wallet extractor
- Password manager (Bitwarden, KeePassXC) stealer
- Browser data collector
The stealer also offers a customizable malware panel and builder, allowing users to tailor the malware's appearance and behavior.
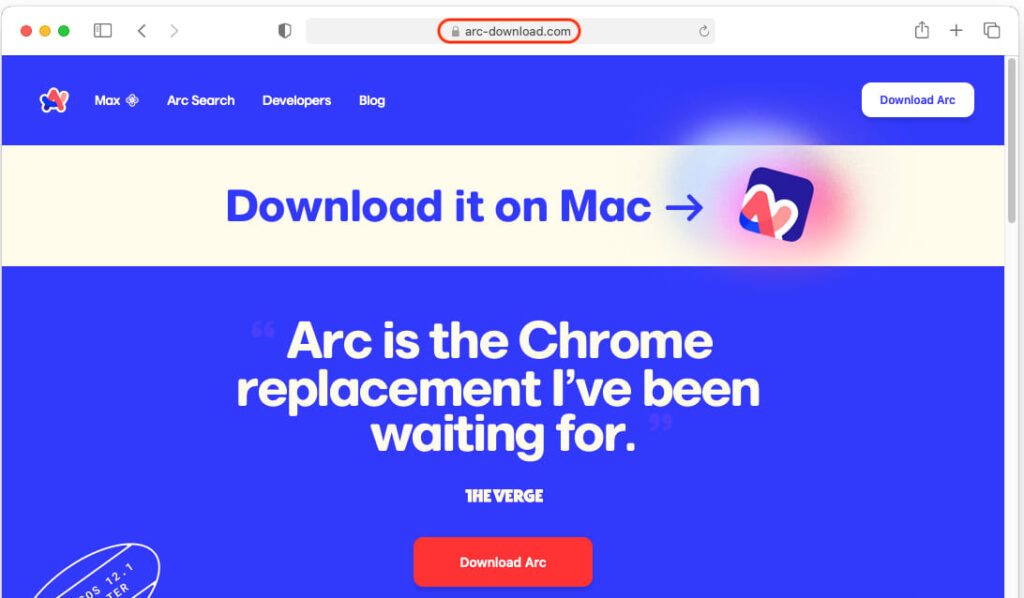
The malicious ads were linked to the domain arcthost[.]org and redirected victims to arc-download[.]com, a decoy site that mimicked the legitimate Arc browser download page. Users who downloaded the offered DMG file were tricked into bypassing security protections via a right-click to open trick. This deceptive technique ensures the malware can be installed without triggering macOS's built-in security measures.
Malwarebytes
Once installed, the stealer sends the exfiltrated data to a command-and-control (C2) server at 79.137.192[.]4/p2p. An analysis of the traffic revealed the use of specific headers such as “uuid: 399122bdb9844f7d934631745e22bd06” and “user: H1N1_Group” to identify and authenticate the data being sent from infected devices.
Poseidon's emergence underscores a growing trend in Mac-focused malware development. The stealer's capabilities pose a significant risk to users, particularly those who manage sensitive information such as VPN configurations and cryptocurrency wallets. Arc browser users are especially targeted due to the browser's rising popularity on that platform.







Leave a Reply