
A severe security vulnerability has been uncovered in the LiteSpeed Cache plugin, a widely used WordPress caching solution with over 5 million active installations. This flaw, identified as a critical privilege escalation issue, allows unauthenticated attackers to gain administrator-level access to websites, posing a significant risk to millions of users.
The vulnerability was first reported by John Blackbourn, a member of the Patchstack Alliance community, to the Patchstack Zero Day bug bounty program, earning him a record $14,400 USD bounty. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-28000, was patched with the release of LiteSpeed Cache version 6.4 on August 13, 2024.
Technical breakdown
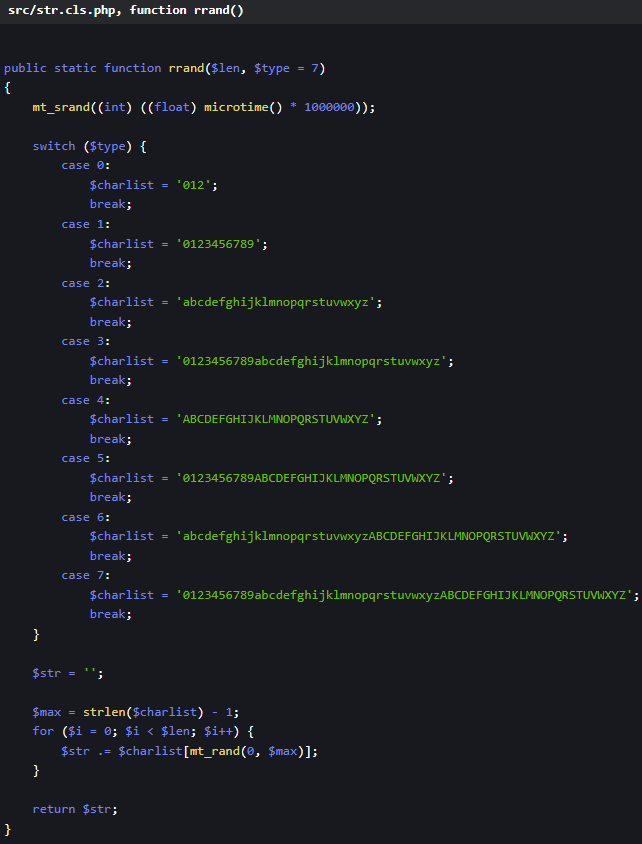
The vulnerability is rooted in the LiteSpeed Cache plugin's user simulation feature, which is designed to allow the plugin's crawler to mimic logged-in users for the purpose of pre-populating cache files. This feature relies on a weak security hash mechanism that is easily exploitable. Specifically, the random number generator employed is seeded with the microsecond portion of the current time, making it predictable and vulnerable to brute force attacks. Additionally, the generated hash is stored in the database and remains constant, further increasing the risk of exploitation.
Patchstack
To exploit the vulnerability, an attacker could trigger the generation of a weak security hash, even if the LiteSpeed Cache crawler feature is disabled. By manipulating an unprotected AJAX handler, the attacker can initiate the creation of the hash and then proceed to brute-force it. Once a valid hash is identified, the attacker can use it to set themselves as an administrator-level user via the wp_set_current_user function, effectively taking over the site.
Impact and response
LiteSpeed Cache is an essential tool for many WordPress sites, offering advanced caching features that significantly improve site performance. The plugin's popularity, combined with the critical nature of this vulnerability, means that potentially millions of sites were at risk before the patch was released. The LiteSpeed team responded promptly, releasing version 6.4 of the plugin, which addresses the vulnerability by implementing stronger hash validation and securing the AJAX handlers against unauthorized access.
The patch introduced the following important changes:
- Implementing a 32-character random hash for security checks.
- Adding a one-time-use hash value that is valid for only 120 seconds.
- Ensuring the security hash is generated anew with each crawler run and tied to the requesting IP address.
Based on stats from WordPress.org, only 24.1% of the plugin's userbase have downloaded the latest version, leaving nearly 3,800,000 sites vulnerable to attacks.
History of exploitation
The LiteSpeed Cache plugin has been targeted by malicious actors before. In a previous wave of attacks reported by WPScan in early May 2024, vulnerable versions of the plugin were actively exploited to inject JavaScript malware into websites, creating backdoor administrator accounts such as “wpsupp-user.” These infections often manifested through malicious code injections in critical WordPress files and databases, allowing attackers to take control of the targeted sites.
Site owners and admins using LiteSpeed Cache are strongly urged to update to version 6.4 or later to protect their sites from potential attacks. If an update is impossible, it is recommended to disable/uninstall the plugin, as the recently patched flaw is critical, potentially leading to complete website takeover scenarios.







Leave a Reply