
Trellix's Advanced Research Center uncovered a series of fake antivirus (AV) websites distributing sophisticated malware.
These sites, masquerading as legitimate AV providers like Avast, Bitdefender, and Malwarebytes, host files with spy and stealer capabilities targeting unsuspecting consumers seeking cybersecurity solutions.
The fake AV sites and malicious identified are:
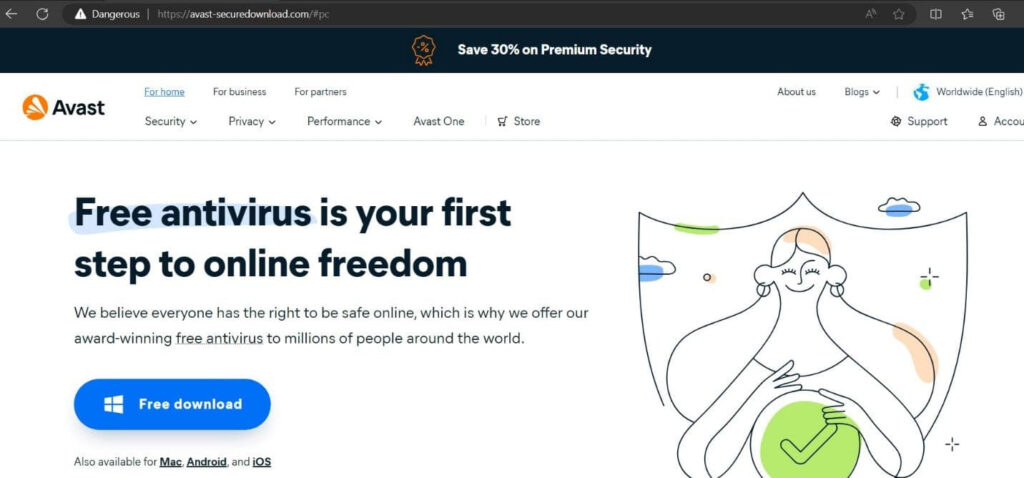
- avast-securedownload.com (Avast.apk)
This Android package (.apk) requests permissions to install/delete packages, access call logs, SMS, contacts, storage data, network state, Wi-Fi state, record audio, and more. It also includes spyware features like screenshot capture, touch activity tracking, and unauthorized program installation. The malware operates a coin miner and location tracker, exfiltrating data to external servers.
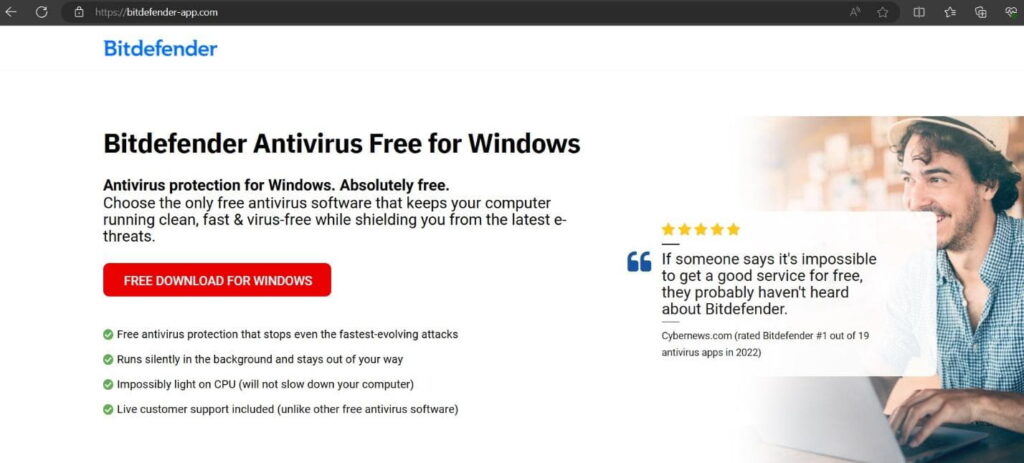
- bitdefender-app.com (setup-win-x86-x64.exe.zip)
The malicious site provides a ZIP file containing a double-extension EXE file. Legitimate software rarely uses such naming conventions, raising initial suspicion. The malware within leverages TLS callback functions and evades detection by injecting itself into “BitLockerToGo.exe”. It collects sensitive information such as PC name, username, hardware ID, login data, browsing history, and more.
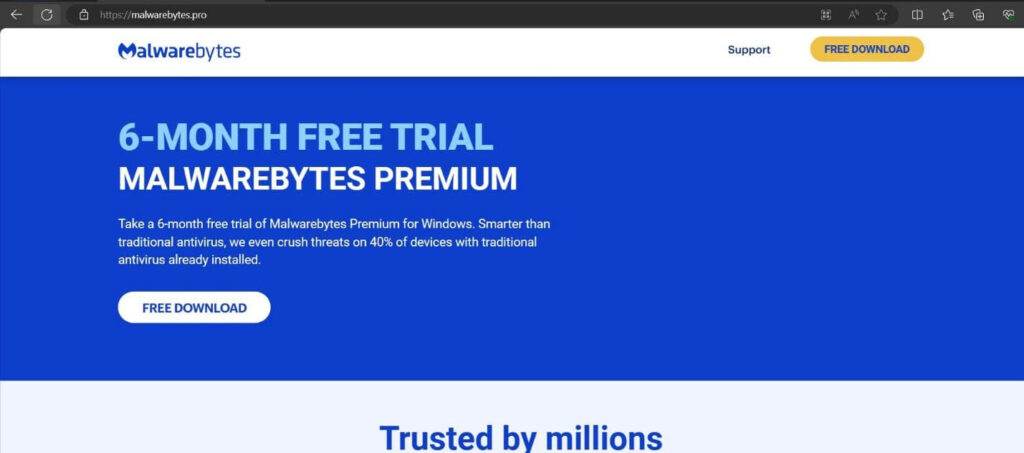
- malwarebytes.pro (MBSetup.rar)
This site delivers a RAR file containing an Inno Setup installer, a readme file, and several legitimate-looking DLLs. Analysis revealed the presence of .NET and C++ payloads encrypted with AES and XOR, respectively. The C++ payload, dubbed “StealC,” exfiltrates data such as account tokens, system profiles, and browser credentials to a command-and-control (C2C) server.
- Malicious Trellix Binary (AMCoreDat.exe)
This binary, disguised as a legitimate Trellix content update file, fragmented its payload across multiple files in the %appdata% directory. It reassembles the payload later, evading antivirus detection. The payload terminates itself if it detects the “avastui.exe” process. If not, it proceeds to steal information such as PC name, username, installed memory, login data, and browsing history.
To safeguard against fake sites distributing dangerous files, always double-check URLs before clicking download buttons on them, ensure their authenticity, and refrain from using pirated software. Additionally, up-to-date internet security suites can detect and block these sites or suspicious file downloads. Whenever you download executables from the internet, make sure to scan them on your AV before launching them.







Leave a Reply