
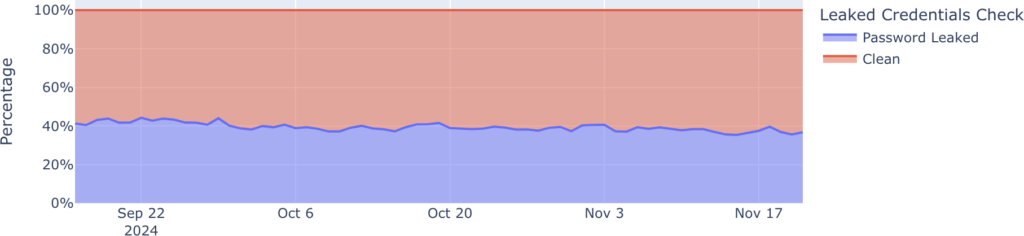
Cloudflare reveals a troubling trend in online authentication, reporting that nearly 41% of successful logins across websites protected by the company involve compromised passwords.
The analysis, based on traffic data from September to November 2024, highlights the widespread issue of password reuse and its exploitation by cybercriminals, mainly through automated credential-stuffing attacks.
Scourge of password reuse
Cloudflare’s study examined authentication attempts on internet properties using its free-tier services, which include leaked credentials detection. The data, drawn from a network encompassing around 30 million websites — roughly 20% of the internet — offers a broad view of online login trends. The analysis focused on leaked passwords, which are credentials exposed in known data breaches and credential dumps.
One of the most striking revelations is that 41% of human login attempts successfully use leaked passwords. This figure underscores the persistent problem of password reuse, which significantly increases the risk of account takeovers. Many users fail to change their passwords even after major breaches or continue using variations of previously exposed credentials, making them easy targets for cybercriminals.
Cloudflare
Adding to the concern, when bot-driven login attempts are factored in, the prevalence of leaked credentials rises to 52% of all authentication requests. Cloudflare’s dataset, which includes over 15 billion leaked credentials from sources such as Have I Been Pwned (HIBP), highlights the sheer volume of compromised passwords still in circulation.
Bots dominate credential-stuffing
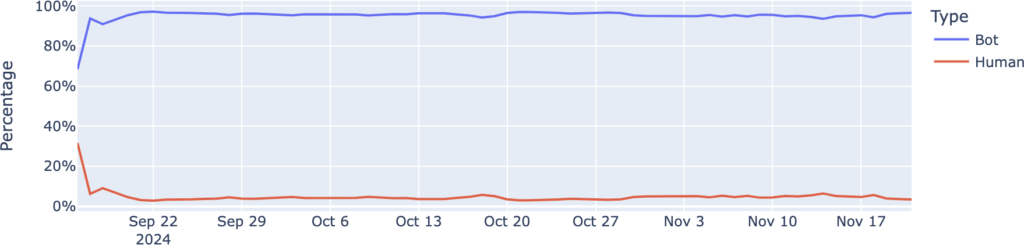
Cloudflare’s report shows that automated bots are the primary culprits in credential-stuffing attacks. A staggering 95% of login attempts using leaked passwords originate from bots, demonstrating the scale at which attackers systematically test stolen credentials against websites. These bots leverage breached username-password pairs, often attempting thousands of logins per second.
Cloudflare
Popular platforms such as WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal are frequent targets, given their widespread use and predictable authentication mechanisms. Attackers often attempt to evade detection by rotating IP addresses and mimicking human-like login behavior. Once a bot successfully gains access to an account, cybercriminals often try to reuse the credentials across multiple services, compounding the damage.
State of WordPress security
WordPress, the most widely used content management system (CMS), accounts for a significant portion of authentication traffic observed in Cloudflare’s network. Due to its standardized login structure, WordPress websites are a prime target for brute-force and credential-stuffing attacks.
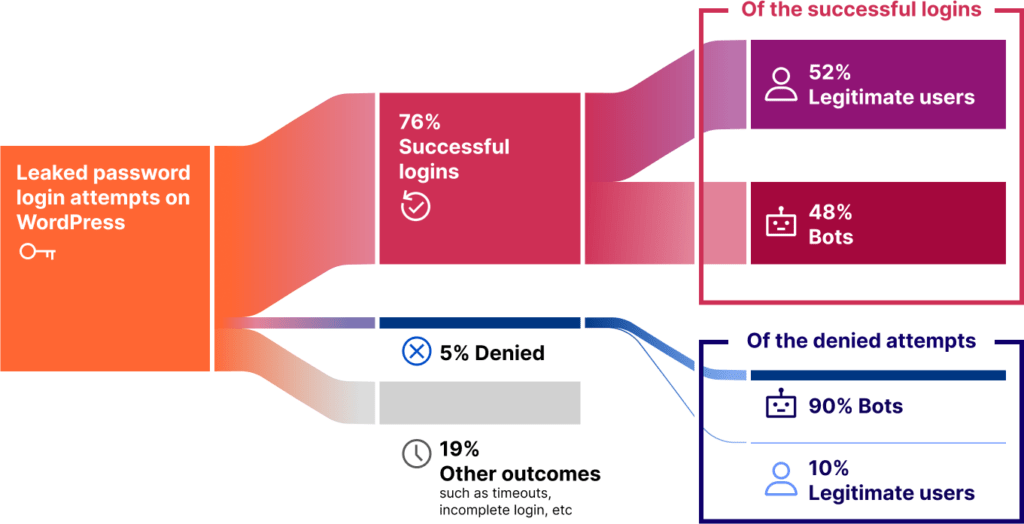
Cloudflare’s data indicates that:
- 70% of leaked password login attempts on WordPress sites are successful.
- 48% of those successful logins are executed by bots.
- Only 5% of leaked password login attempts result in access being denied.
These statistics highlight how poorly secured many WordPress sites remain, particularly when lacking measures such as rate limiting or multi-factor authentication (MFA). With unauthorized logins forming nearly half of all successful authentication attempts, the risk of account takeovers on WordPress sites is alarmingly high.
Cloudflare
Mitigation strategies
Cloudflare’s report emphasizes the need for stronger authentication practices to counter the threat posed by leaked credentials. Both individuals and organizations must take proactive steps to secure their accounts and online services.
Users are recommended to use unique, strong passwords for every account and enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) wherever possible. Also, passkeys should be considered as a more secure, phishing-resistant alternative to traditional passwords.
Website owners should activate leaked credential detection, enforce password resets when compromised credentials are detected, and implement rate limiting and bot management tools to curb automated attacks.







Leave a Reply