
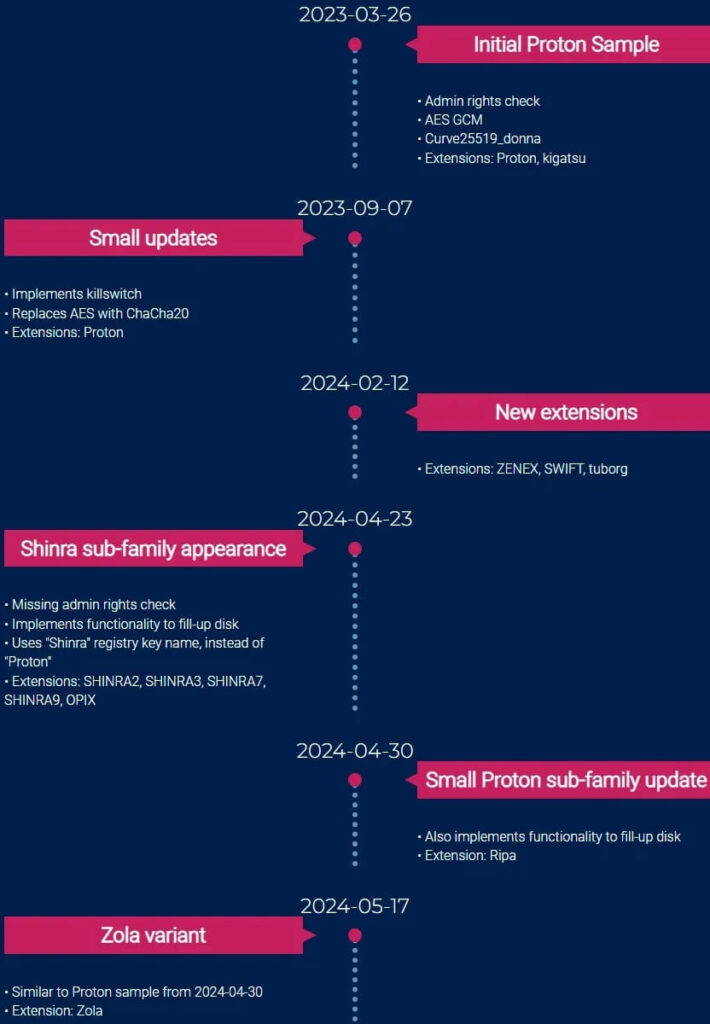
The Zola ransomware, initially appearing as a novel threat, has been identified as a rebranded variant of the Proton family, according to the Acronis Threat Research Unit. Proton, first discovered in March 2023, continues to evolve through various iterations, with Zola being its latest manifestation.
Discovery
The Acronis Threat Research Unit uncovered Zola during an incident response session. The ransomware, compiled on May 17, 2024, exhibits typical behaviors of the Proton family. It utilizes several older but effective tools to escalate privileges, scan networks, and steal authorization tokens before deploying its payload.
The tools identified include Mimikatz 2.2.0, ProcessHacker 2.39, Sysinternals Process Explorer 16.42, and Advanced IP Scanner 2.5.3850. These tools are often dropped in user directories like “Downloads,” “Music,” or “3D Objects.”
Technical details and behavior
The Zola executable, about 1 MB in size and developed in C++, creates a mutex named “4B991369-7C7C-47AA-A81E-EF6ED1F5E24C” to prevent concurrent execution, a hallmark of Proton variants. It checks for administrative rights and has a kill switch that terminates the process if a Persian keyboard layout is detected.
Zola's encryption phase is preceded by several preparatory steps:
- Generation of victim ID and key information stored in registry values under HKCU\Software\Proton\public and HKCU\Software\Proton\full.
- Changing the system wallpaper and setting registry values like “legalnoticecaption” to display custom messages during login.
- Deleting shadow copies using commands like “cmd /c vssadmin Delete Shadows /All /Quiet” to hinder data recovery.
- Modifying boot configurations with BCDEdit commands to disable automatic repair and force Windows to ignore all failures.
Before encryption, Zola copies itself to the user's Startup folder using the victim ID as the filename and attempts to terminate 137 processes and 79 services to facilitate the encryption process.
Encryption scheme
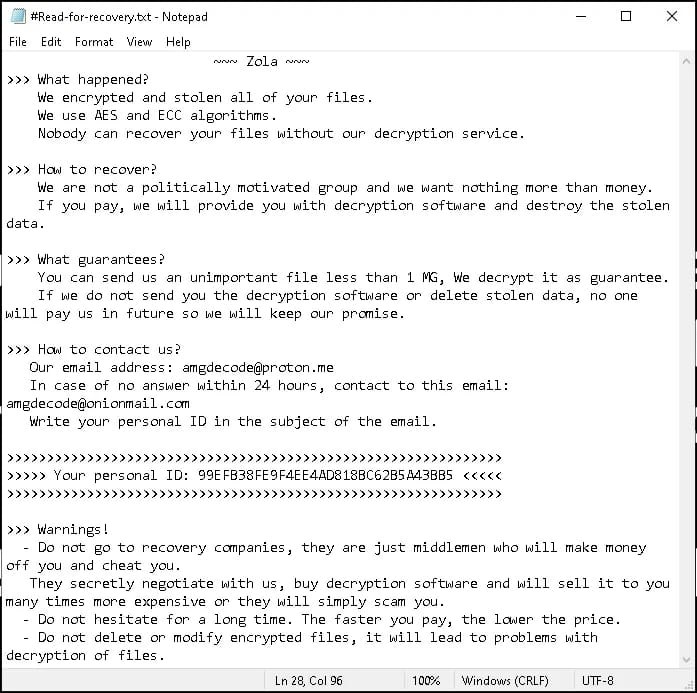
Zola employs an encryption scheme that initially used an elliptic curve (curve25519) for key derivation and AES in GCM mode for file encryption. However, since September 2023, Proton variants, including Zola, have transitioned to using ChaCha20 for encryption. The ransomware also drops a ransom note in each folder, directing victims to contact amgdecode[@]proton[.]me or amgdecode[@]onionmail[.]com for recovery instructions.
Acronis
Impact and protection
Since its emergence in March 2023, Proton has seen numerous rebranded versions, maintaining its core functionality while occasionally introducing minimal codebase changes. The continued prevalence of both x86 and x64 variants indicates that attackers are targeting a wide range of systems, including older x86-based ones.
Acronis
As a general advice against ransomware threats, Acronis recommends using endpoint and real-time protection tools and regularly backing up important data in offline or network-isolated systems. Additionally, activate multi-factor authentication to protect administrative accounts, implement network segregation, and keep all systems up to date.







Leave a Reply