
Most password managers look and feel the same: Polished dashboards, tiered pricing, and a smooth setup process that works for everyone from casual users to enterprise teams. KeePass, however, takes a very different approach.
It doesn’t try to dazzle you with slick visuals or hand-holding onboarding. In fact, some might even say it’s a little intimidating at first glance. Yet once you get past that initial wall, you may discover one of the most powerful, flexible, and customizable password managers on the market.
So, what makes KeePass stand out in a sea of competitors? The secret lies in its open-source nature, unmatched control, and the ability to bend the software entirely to your needs — but there’s also a catch. Jump to why that makes KeePass unique.
| Website | Keepass.info |
| Platforms | Windows, macOS, Linux, Android, iOS |
| Browser extensions | Only via plugins |
| Free version | Yes |
| Encryption | SHA-256 |
| Support | Community forum |
| Price | Forever-free |
If you think that KeePass is worth a look, here’s a short list of its main pros and cons:
+ Pros
- 2FA and MFA support
- Completely free and open-source software
- Uses strong, local-only encryption methods
- Allows easy import from other managers
- Regularly updated despite being decades old
- Data encrypted in transit and at rest
- Multiple sync strategies are available
- Highly customizable with third-party plug-ins
- Wide variety of powerful plugins
– Cons
- Limited customer support, mostly forums
- Not particularly beginner-friendly
- Setup can be time-consuming
- Officially available only on Windows
- Outdated UI
KeePass feature summary

KeePass core features at a glance:
- End-to-end encryption with AES-256, ChaCha20, Argon2
- Full database encryption, local storage only
- Cross-platform support (Windows, Linux, macOS, BSD)
- Multi-language interface (45+ languages)
- Strong built-in password generator
- Import/export in TXT, HTML, XML, CSV
- Supports 2FA/MFA for extra security
- Wide range of plugins for customization
- Flexible sync options for backups
Company information
KeePass isn’t published by a company. It is free and open-source (FOSS) software distributed under the terms of the GNU General Public License version 2 or later by the author, Dominik Reichl.
As often happens with FOSS software, while the core product is created and maintained by Mr. Reichl, much of the KeePass software is actually created and maintained by others.
Terms, conditions, and privacy policy
The legal verbiage for KeePass is all available here in English and German. The portion of the document covering Privacy appears to comply with the EU’s GDPR (if you want to be sure, check for yourself).
KeePass does collect some user data. Session-related data is deleted at the end of the session. Some data is collected in logs. The data in the logs is either deleted after at most seven days, or anonymized if kept longer.
Third-party audits

Given that third-party audits are expensive, and KeePass is free, I didn’t expect to find any such audits. However, as you can see on the Awards, Ratings, and Opinions page, KeePass was audited twice, most recently in 2016. This last was a code review by the EU’s Free and Open Source Software Auditing project, also known as EU-FOSSA 1.
While it would be great to see penetration testing results on KeePass, this code audit, along with the various other audits and awards on this page, are all positive signs for KeePass.
KeePass clients
There are KeePass clients for most operating systems and web browsers. Here’s what the Windows version looks like:
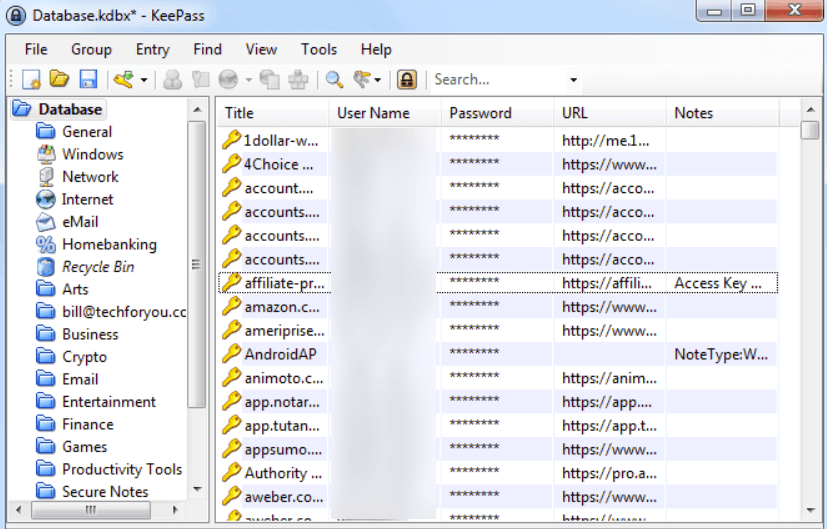
The user interface for KeePass doesn’t appear to have changed much since the birth of the product back in 2003. It appears that the developer has put his effort into improving the functionality of KeePass rather than the appearance. Given that he is a one-man band, as it were, that approach makes a lot of sense.
Interestingly, only the Windows version is actually published by Mr. Reichl. All other clients are unofficial releases created by third-party developers. That can be confusing, but it also allows the KeePass ecosphere to evolve much faster than if one person had to do everything himself.
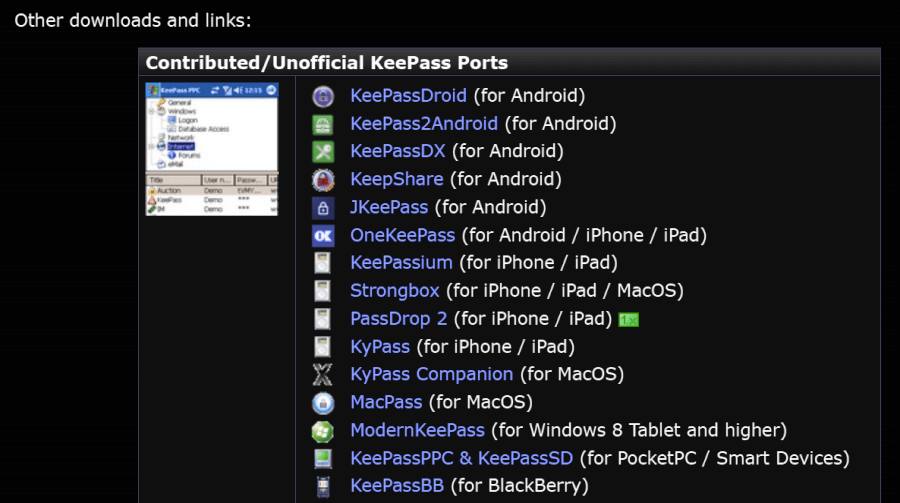
So how do you know which client to use? Your best bet is to go to the KeePass downloads page and try out any of the Contributed/Unofficial KeePass Ports you find there for the device you are interested in.
Whether you’re on a major OS, a web browser, or a niche device like Windows Phone or Sailfish, KeePass has you covered.
KeePass hands-on testing
I tested KeePass on an old Windows 7 machine. Since KeePass isn’t set up to sync between multiple devices by default, I did not attempt to set this up.
There are several approaches you can use, involving various levels of manual configuration. If you decide to use KeePass on multiple devices, you’ll need to go to this page to learn about how KeePass synchronization works and configure one of the sync methods yourself.
Installing KeePass
I downloaded the installer for KeePass 2.43 from the Downloads page and ran that. The installation was pretty standard at first, but became a bit confusing when it required me to specify where the passwords should be stored and what the file should be called, followed by creating a Composite Master Key:
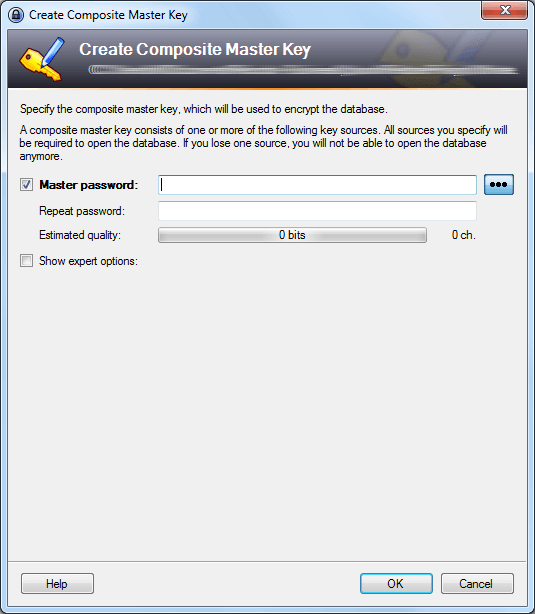
I can see a typical user throwing up their hands at this point and deciding to try a different product.
After creating the Composite Master Key (which is required to get access to your stored data) I was able to view the empty Windows client, which looks like this:
Adding login credentials to KeePass
With the client up and running, it was time to add some login credentials. KeePass gives you two ways to add login credentials.
- Import credentials from your web browser or another password manager;
- Enter credentials manually.
Unfortunately, KeePass does not have a feature to capture login credentials. You need to enter the data manually whenever you log in to a site and the data isn’t already in KeePass. While this approach gives you complete control over what and how gets added to KeePass, you may find this to be more of an annoyance than a feature.
Importing login credentials
KeePass can import data from numerous other password managers, as well as Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox. I tested this capability by importing all my data from Bitwarden. The process only took a couple of minutes and even replicated my Bitwarden folder structure so all my passwords and notes remained organized.
Adding login credentials manually
To add login credentials manually, open KeePass and click the Add Entry button, or press the CTRL+I keyboard shortcut. The Add Entry window appears, and looks like this:
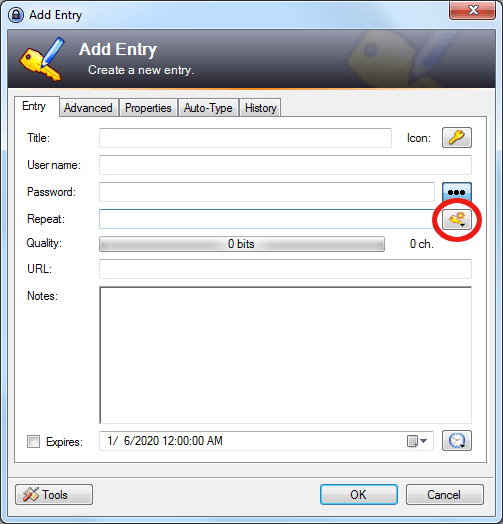
Enter the username and password you want to use in the provided fields. KeePass will generate a Quality score for the password you enter, making it easy to ensure that you don’t create a weak one.
The best way to avoid creating weak passwords is to use the KeePass Password Generator. Click the Generate a Password button (circled in red in the preceding image) and in the menu that appears, select Open Password Generator.
KeePass password generator
The password generator in KeePass is packed with options, giving you full control to create strong passwords without hassle.
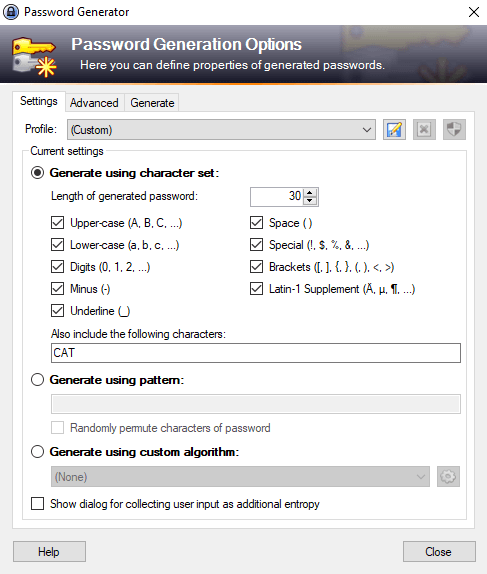
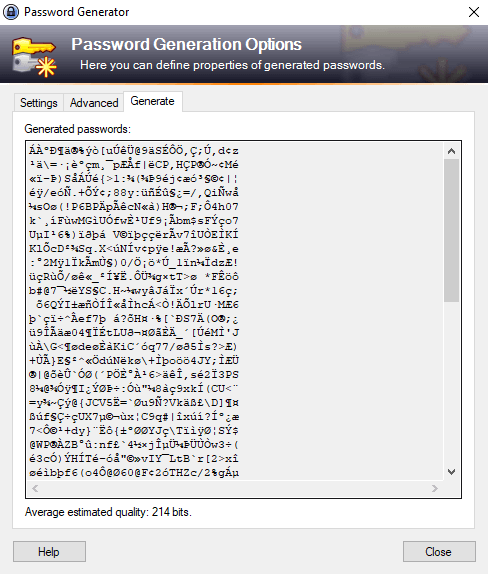
Most of the time, KeePass defaults are enough for strong passwords — here’s a quick example it generated:
Auto-type to fill in fields
Wait! We’re not done yet.
KeePass takes a very different approach to enter your data into a web page than other password managers. Whereas they just automatically enter the data into the relevant fields on the page, KeePass Auto-Types on the page.
The system is a little complicated, but the idea is that you give KeePass the exact sequence of keystrokes you would use if you were logging into the site by hand. You program this sequence of keystrokes on this tab in the Add Entry window:
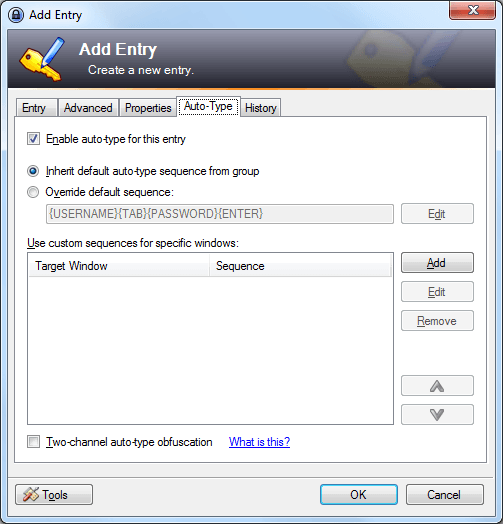
This may seem like a crazy way to do things. It does make setting up most passwords harder than with other products. The benefit is that you can set up KeePass to work with virtually any login screen, no matter how complicated. You’ll have to decide for yourself whether this is a benefit or a reason to look elsewhere.
Working with your passwords and other data
Once you’ve got login credentials and other data into KeePass, how do you work with that data? Open up KeePass and select the database that contains the data you want to work with. All the data entries are visible when you select the database itself. Or you can select the folder that contains the type of data you are looking for (Secure Notes, for example), and find the correct entry there.
Double-click the entry to open the Edit Entry window. The window is virtually identical to the Add Entry window we looked at earlier, which means you can view or edit anything about that entry in this window.
KeePass in action
To get KeePass to enter your login credentials onto a web page, you need to do a bit more work than with other password managers. Since it is a standalone app instead of a browser extension, you have to tell KeePass what page it needs to fill in.
To get KeePass to enter your Login Credentials, follow these steps:
- In your web browser, navigate to the page you want to log into.
- Open KeePass, and select the entry for that page.
- Click the button circled in red in the following image:
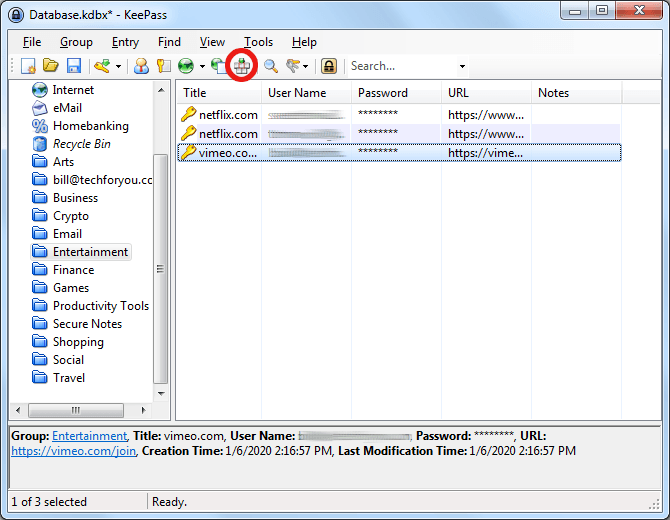
Once you do this, you will see KeePass literally type the data into the appropriate fields and log you in.
Additional KeePass features: A quick look
I’ve found that KeePass goes far beyond simple password storage. With more than 100 plugins and extensions, it can be shaped to fit almost any workflow, from browser autofill to running as an SSH agent. In our experience, if you imagine a feature you’d like, there’s probably already a plugin for it.
The latest release, KeePass 2.59 (July 2025), really shows how the project keeps evolving. We noticed smoother performance, faster encryption, and better integration across platforms, plus the peace of mind of signed binaries and updated translations. It even runs natively on Windows 11 ARM64, which is a nice touch.
Features like Secure Desktop, process memory protection, and clipboard clearing add layers of defense against keyloggers. Paired with Auto-Type, the password generator, file attachments, and detailed password reports, KeePass feels like a powerful manager that adapts as your needs grow.
The evolution of KeePass
KeePass began its life as a Windows-only program, built in C# and dependent on Microsoft’s .NET framework. While powerful, this dependency made porting KeePass to other operating systems tricky, often leaving it looking like an outdated Windows app rather than a native Mac or Linux tool.
To address this, developers launched KeePassX in the mid-2000s, originally known as KeePass/L, as a Linux-friendly version. By 2006, it had evolved into a cross-platform application. However, active development came to a halt in 2016.
Not wanting the project to fade, a community of fans picked up where KeePassX left off, creating KeePassXC, a fork that continues to bring KeePass features to users across Windows, macOS, and Linux with a more modern approach.
Meet KeePassXC: The KeePass cross-platform community edition
Here’s how the developers describe KeePassXC:
“KeePassXC is a community fork of KeePassX, a native cross-platform port of KeePass Password Safe, with the goal to extend and improve it with new features and bugfixes to provide a feature-rich, fully cross-platform and modern open-source password manager.”
To make this happen, KeePassXC is written in C++, which makes it possible to run natively on Windows and non-Windows operating systems.
KeePassXC can read KeePass password databases, making it easy to migrate your passwords over. That said, they are definitely distinct products. The following table lists some of the differences:
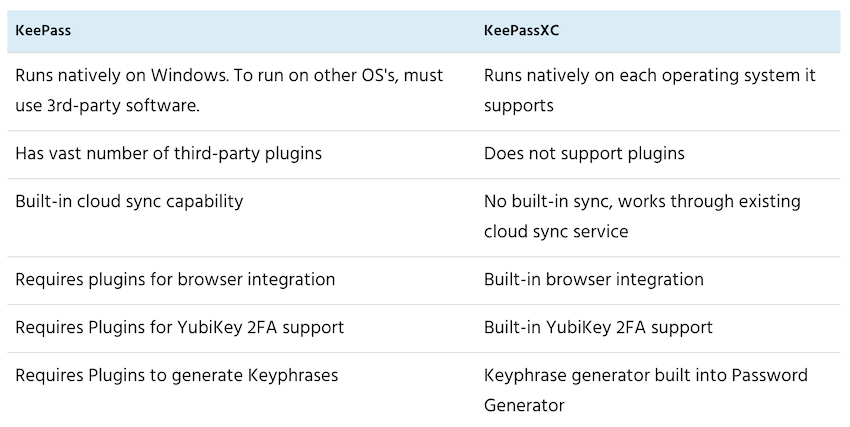
You can consider KeePassXC as a great alternative to KeePass if you want to run your password manager on multiple operating systems, or you need one of the features in the preceding table. You might also want to consider that KeePassXC is being developed by a team (five members currently), while KeePass is a one-person project.
KeePass support
Since KeePass is created and maintained by the author, there isn’t a support team like you would get with other password managers, such as Dashlane. That means no phone support, no Twitter, and no email. If you need help with KeePass, the place to get it is in the KeePass forum on SourceForge.
The other resource you can use if you have problems is the KeePass Help Center.
There is a lot of detailed information here about every aspect of the product. However, much of the information is pretty technical, and may be somewhat confusing for regular users.
Is KeePass secure and private?
KeePass is designed with strong security and privacy in mind. Your data is stored locally in an encrypted database, and the software includes multiple layers of protection to safeguard against common threats.
Security
Core security features include:
- AES-256, ChaCha20, and Twofish encryption for your database
- Master password, key file, and Windows user account options
- Argon2 or AES-KDF for strong protection against brute-force attacks
- Secure Desktop and process memory protection
- Built-in password generator and Auto-Type
- Clipboard clearing and plugin support for extra security
With these protections, KeePass gives you a secure, flexible, and privacy-focused password manager.
Privacy
As we saw during my review of the Privacy Policy, KeePass does collect some data and can hang onto it for a little while. But this is pretty standard, and as the policy says, the data they log is the minimum needed to make the site function. Even this minor risk is mitigated by two points:
- KeePass is open-source software. Anyone can examine the code. Since KeePass has an active community of users and developers, it seems likely that someone would notice if there was anything objectionable in the code.
- There is no KeePass corporate cloud where your data is stored. About all someone can determine from an attack on KeePass is that you have an account.
How much does KeePass cost?
Nothing. Zip. Nada. That’s right, KeePass is totally free, and so is KeePassXC. However, if you appreciate the work they are doing, both teams will accept donations.
Is KeePass right for you?
KeePass isn’t for everyone. Its extreme flexibility and power make it a fantastic tool, but that same strength comes with complexity. Setting it up, configuring plugins, and managing databases can feel daunting if you’re not technically inclined.
On the plus side, KeePass is open-source, highly secure, and endlessly customizable. You can create strong passwords, enable Auto-Type, attach files, and even integrate it with browser extensions or SSH keys. The downside? It lacks the polished, user-friendly experience of commercial password managers, and support relies mostly on self-help guides and community forums.
If you enjoy tinkering, value full control over your security, and want a manager that can grow with your needs, KeePass can be an incredibly rewarding choice. Its flexibility and strong security make it a standout for tech-savvy users.
KeePass Alternatives
If KeePass doesn’t quite fit your needs, NordPass is a great place to start. It’s simple, secure, and works seamlessly across all your devices — perfect if you want something easy to use without sacrificing safety.
For those who love the open-source nature of KeePass but find it too complex, Bitwarden offers a simpler, user-friendly alternative while still being open-source.
And if you want a feature-packed experience like KeePass but with less complexity, Dashlane delivers robust tools and ease of use, though it isn’t open-source.
KeePass FAQ
KeePass is very secure when used properly. It stores your passwords in an encrypted database, protected by a master password, key file, or both. Extra features like Secure Desktop, process memory protection, clipboard clearing, and Auto-Type help guard against keyloggers and other attacks. While no system is 100% foolproof, KeePass gives you strong protection and full control over your data.
KeePass 1.x is the original version with a simpler design, while KeePass 2.x adds more advanced features, better encryption, and broader plugin support. KeePass 2.x is also cross-platform compatible through additional tools, which makes it a better choice for most users who want flexibility and modern functionality.
Yes! KeePass is completely free to download and use. Being open-source means its code is publicly available for anyone to review, improve, or build on. This transparency also contributes to its security, as vulnerabilities can be spotted and fixed by the community.
Backing up your KeePass database is simple: Just make a copy of your .kdbx file and store it in a safe location, like an external drive or cloud storage you trust. To restore, simply open the backup file in KeePass. For added safety, you can also use the built-in backup options in KeePass 2.x to automatically save previous versions of your database.
Wrapping up our KeePass review
KeePass is a powerful password manager, but it’s really designed for tech-savvy users. On a single computer, it offers rock-solid security and virtually unlimited customization through plugins—but for those who prefer simplicity, it can feel a bit overwhelming.
If you’re comfortable tweaking settings and exploring advanced features, KeePass shines. Its active community, flexible plugin system, and robust security tools let you build a setup that fits almost any workflow or organization.
For anyone who wants cross-platform compatibility, KeePassXC is a solid alternative. It’s easier to use and works on multiple operating systems, though it comes with some limitations. In short, KeePass is a gem for tech enthusiasts, while casual users might prefer something like NordPass or Bitwarden for a smoother, more user-friendly experience.
And if you wish to check some of KeePass’s competitors, here is the full list of our password manager content:

That’s wrong completely. Just try to open/work/change actively same kxdb file on different machines or OS’es. Will soon regret your choice. And see the advantage of KeePass sync feature. For this reason a cross-platform compatibility of KeePassXC goes to nothing.
Bets regards.