
Google has patched another zero-day vulnerability in the Chrome web browser, which was found to be actively exploited by hackers in the wild.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2024-7971, was discovered and reported by Microsoft's Threat Intelligence Center (MSTIC) and Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC) on August 19, 2024, and has been fixed in the newly released Chrome version 128.0.6613.84.
Technical details
The vulnerability, classified as a high-severity issue, stems from a type confusion error within Chrome's V8 JavaScript engine. Type confusion flaws occur when a program incorrectly handles data types, leading to unpredictable behavior. In this case, the bug allows for heap corruption, a memory management error that can be leveraged by an attacker to execute arbitrary code on a victim's machine. This type of exploitation can be particularly dangerous as it grants attackers the potential to take control of an affected system, bypassing security measures and installing malicious software.
The flaw was identified in Chrome's V8 engine, which is responsible for executing JavaScript code in the browser. An attacker could exploit this vulnerability by luring a user to visit a specially crafted HTML page. Once the page is opened in Chrome, the browser could be manipulated to execute harmful code without the user's knowledge. Given the widespread use of JavaScript in web applications, such a vulnerability poses a significant risk to users.
The urgency of the patch is underscored by the fact that Google acknowledged an exploit for CVE-2024-7971 being used in active attacks. Although details of the ongoing exploitation have been kept under wraps to prevent further abuse, the existence of such an exploit highlights the critical nature of the vulnerability and the need for users to update their browsers immediately.
If left unpatched, this vulnerability could allow attackers to take full control of a compromised system. Depending on the attacker's intent, this could lead to a range of malicious activities, including data theft, ransomware deployment, or even using the compromised machine as part of a larger botnet. The severity of the issue is compounded by the fact that browsers like Chrome are used by millions worldwide, making them prime targets for cybercriminals.
Fix available
Google has responded promptly by releasing Chrome version 128.0.6613.84 for Windows, Mac, and Linux users, which includes the fix for this zero-day vulnerability along with 37 other security fixes. Users are strongly advised to update their browsers as soon as possible to protect against potential attacks.
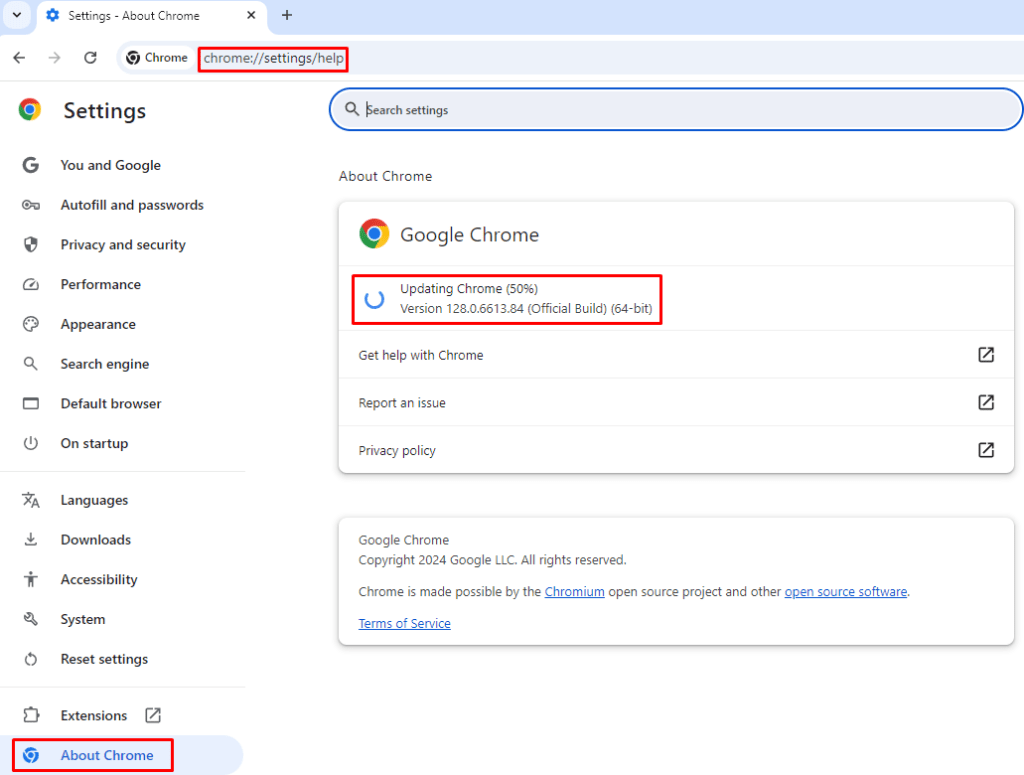
To update Chrome:
- Click on the three vertical dots in the upper-right corner of the browser.
- Navigate to “Help”> “About Google Chrome.”
- Chrome will automatically check for updates and begin downloading the latest version.
- Once the update is downloaded, click “Relaunch” to complete the installation.
Regularly updating your browser is essential for maintaining security, as it ensures that known vulnerabilities are patched and new features are installed. In addition to updating Chrome, users should remain vigilant against suspicious links and websites, particularly those received through unsolicited emails or messages.







Leave a Reply