
AmberWolf, a security research group, has revealed significant vulnerabilities in widely used corporate VPN clients through their new tool, NachoVPN. Announced at the SANS HackFest Hollywood 2024, NachoVPN demonstrates how attackers can exploit trust weaknesses in VPN clients to gain remote code execution (RCE) and elevated privileges. The research highlights critical risks in popular tools like Palo Alto GlobalProtect and SonicWall NetExtender.
Corrupting VPN updates
AmberWolf's investigation focused on how VPN clients trust servers by default, revealing weaknesses attackers can exploit. This implicit trust allows rogue VPN endpoints to deliver malicious updates, install fake certificates, and compromise user credentials. Their research covered SSL-VPN clients and modern Zero Trust solutions, with practical attack simulations demonstrating real-world impact on enterprise environments.
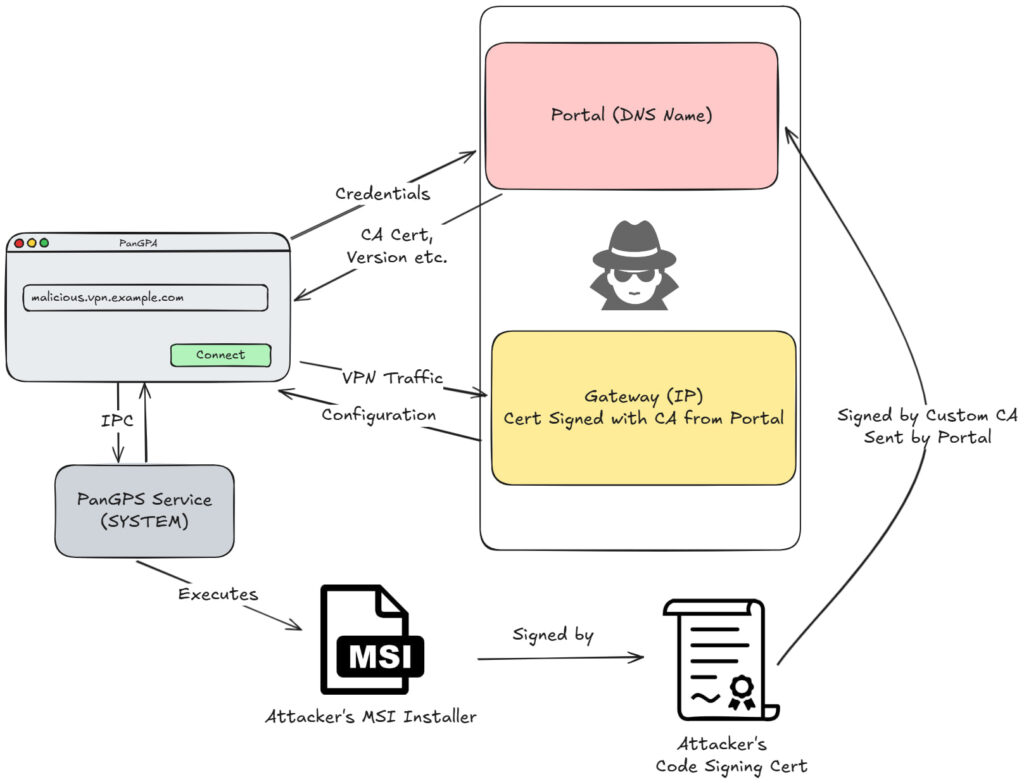
One major finding involved the GlobalProtect VPN client from Palo Alto Networks. By leveraging configuration flaws, attackers could install malicious root certificates, execute code with SYSTEM-level privileges, and fully compromise devices. Similar vulnerabilities were discovered in SonicWall's NetExtender client, where attackers could bypass update validation mechanisms to execute arbitrary code.
AmberWolf also introduced NachoVPN, an open-source proof-of-concept tool to simulate these attacks and aid in understanding and mitigating the risks. The tool adapts to different VPN clients, demonstrating how attackers can manipulate client behaviors across platforms.
The vulnerabilities disclosed by AmberWolf are:
Palo Alto GlobalProtect (CVE-2024-5921) – Both macOS and Windows clients are affected. Exploitable through malicious VPN servers, allowing attackers to install fake root certificates and push updates. Leads to full system compromise via privilege escalation.
AmberWolf
SonicWall NetExtender (CVE-2024-29014) – Affects Windows clients. Attackers can deliver fake EPC Client updates, bypassing signature checks. Results in RCE with SYSTEM privileges.
Both vulnerabilities allow attackers to manipulate critical VPN functions, exposing enterprises to significant risks.
Mitigations and vendor responses
AmberWolf followed responsible disclosure procedures, notifying affected vendors in early 2024. Palo Alto Networks eventually introduced mitigations, such as stricter certificate validation, but the fix required manual configuration changes. SonicWall patched its NetExtender client in June 2024 after addressing AmberWolf's feedback.
To defend against these vulnerabilities, organizations are advised to:
- Update VPN clients to the latest secure versions.
- Enforce stricter validation settings, such as Palo Alto's FULLCHAINCERTVERIFY.
- Restrict endpoints VPN clients can connect to using firewall rules.
VPN clients are a cornerstone of corporate network security, but AmberWolf's findings underscore how trust assumptions in client-server relationships can be exploited. NachoVPN not only reveals these risks but also provides a platform for researchers to explore potential mitigations and prevent similar flaws in the future.
While patches are now available for these vulnerabilities, the research highlights the need for proactive security measures and regular updates to protect against evolving threats.







Leave a Reply