
New research has revealed a significant vulnerability in the NAT port preservation strategy and the insufficient reverse path validation strategy employed by WiFi routers.
The newly discovered side-channel vulnerability allows off-path attackers to intercept and manipulate TCP connections within the same network, leading to potentially severe security breaches.
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a method used in networking that allows one or more local IP addresses to be translated into one or more global IP addresses and vice versa. This process enables multiple devices on a private network to access the internet using a single public IP address. NAT plays a crucial role in conserving global address space, providing a type of firewall by hiding internal IP addresses, and allowing for the private IP space to be used inside organizations and networks.
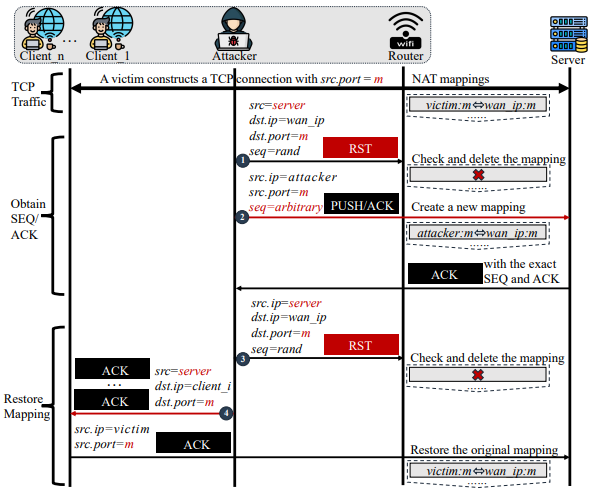
The research, conducted by researchers at American and Chinese universities, demonstrates that an attacker can infer active TCP connections between clients within a WiFi network and external servers. By exploiting the vulnerability, attackers can displace original NAT mappings at the router, allowing them to intercept server responses, hijack TCP connections, and inject malicious data into the communication stream.
arxiv.org
This vulnerability is particularly concerning due to the widespread use of WiFi networks in various public and private settings, posing a risk to the confidentiality and integrity of data transmission.
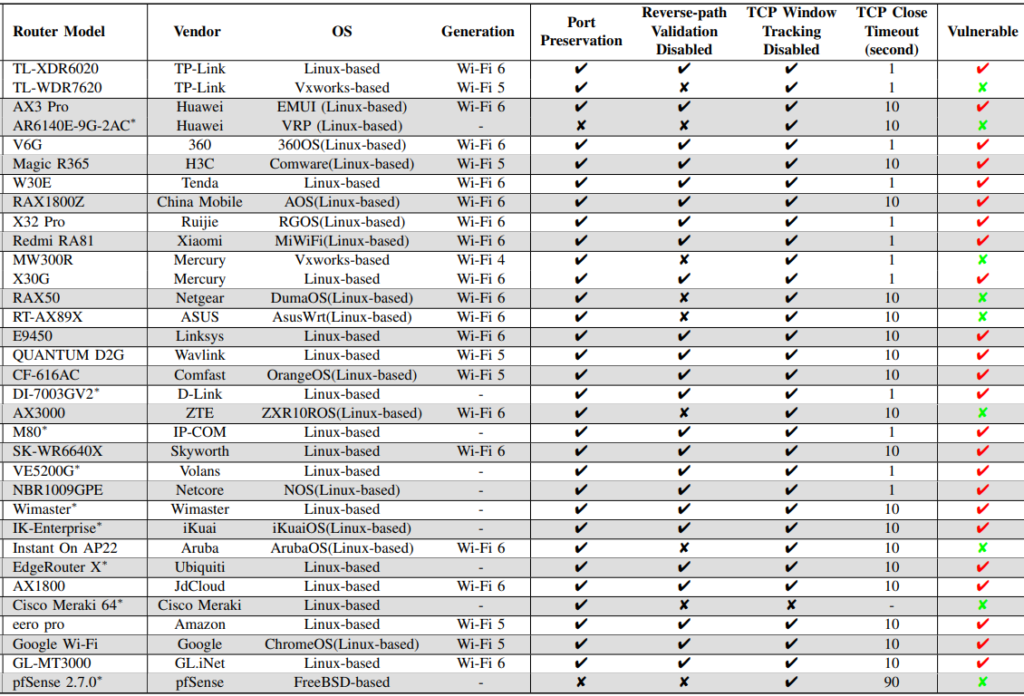
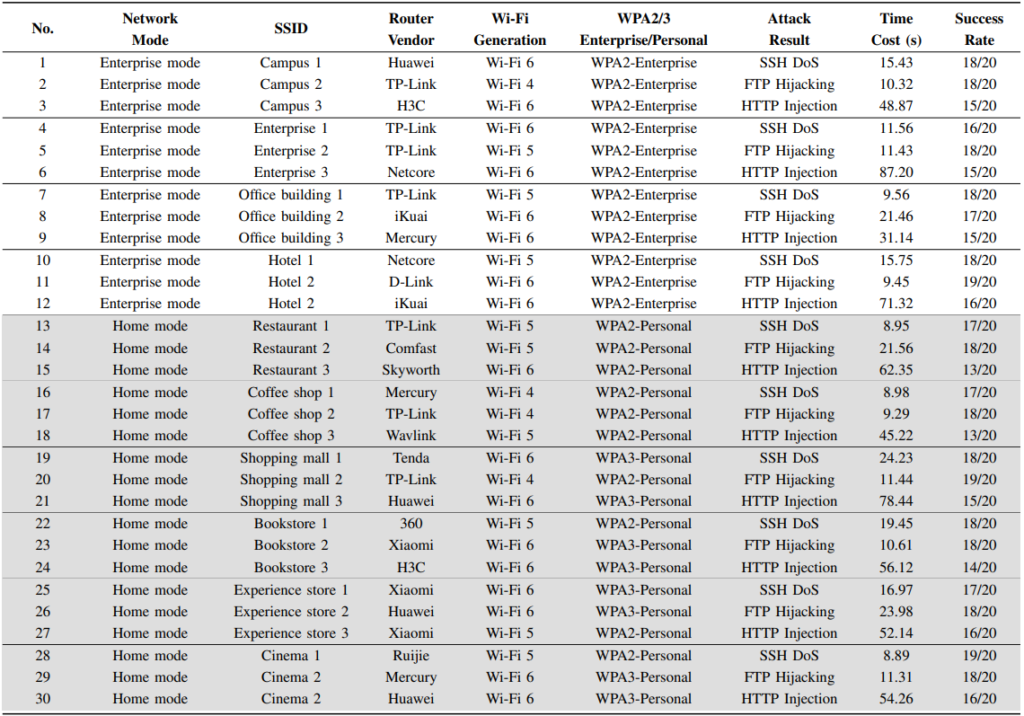
The study examined 67 widely used routers from 30 vendors, discovering that 52 of them are susceptible to this form of attack. Moreover, an extensive measurement study on 93 real-world WiFi networks showed that 75 (81%) of these networks are fully vulnerable.
arxiv.org
The researchers' successful execution of attacks, including the termination of SSH connections, unauthorized downloading of private files from FTP servers, and injection of fake HTTP responses, within seconds, underscores the real-world implications of this vulnerability.
arxiv.org
The researchers have proposed a range of crucial countermeasures to mitigate this vulnerability in the technical paper. These include enabling strict mode reverse path validation, implementing dynamic NAT port allocation strategies, and bolstering the security features of TCP connections. Their responsible disclosure of findings to affected router vendors has already led to positive responses and the adoption of some of these recommended strategies.
In conclusion, the findings of this research offer critical insights into a previously overlooked security vulnerability within NAT-enabled WiFi networks. Users are recommended to apply the latest available firmware updates for their devices to ensure that they have the latest security updates, change the default admin password on their routers, and regularly monitor settings to catch any unauthorized changes quickly.







Leave a Reply