
Meta has launched key transparency for end-to-end encrypted (E2EE) chats on Messenger, enabling users to automatically verify the authenticity of their contacts’ encryption keys.
This new feature enhances the platform’s existing E2EE framework by adding a crucial layer of protection against key tampering, marking a significant milestone in securing private communications at scale.
The feature builds on similar efforts seen in WhatsApp, which implemented key transparency in 2023. By extending this architecture to Messenger, Meta has delivered a solution that ensures the integrity of encryption keys used in chats, even in a multi-device environment where keys frequently change.
Key transparency is a security mechanism that maintains a verifiable, tamper-evident record of public keys used for encryption. In practical terms, this helps prevent so-called key substitution attacks, where a malicious actor, potentially even an insider with access to backend systems, could silently replace a recipient’s encryption key with one under their control. With key transparency in place, users gain confidence that messages are genuinely encrypted for the intended recipients and not intercepted through manipulated cryptographic credentials.
Messenger, Meta’s widely used messaging platform with over a billion users, has gradually introduced end-to-end encryption across chats and calls in recent years. Unlike simple key fingerprint comparisons between users, which can be cumbersome, especially when devices are frequently added or re-registered, the new key transparency feature automates this process, reducing the need for manual verification while still preserving the option for advanced users who prefer it.
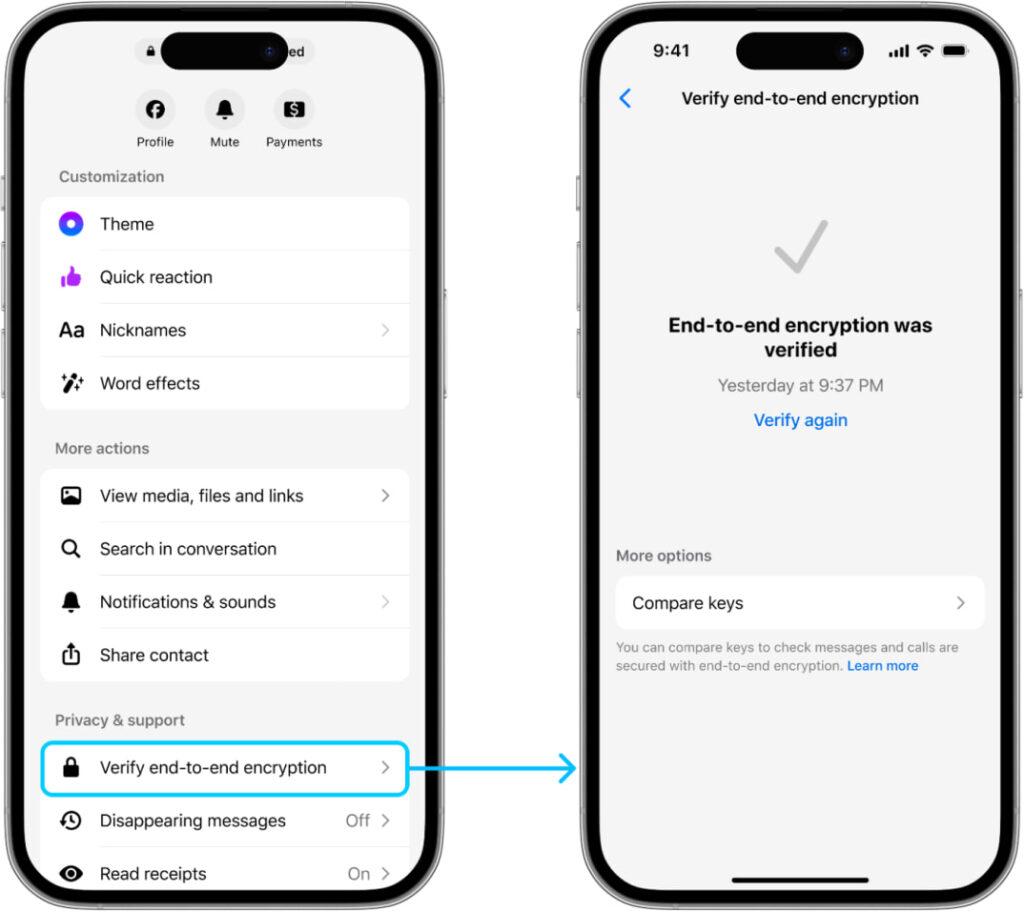
To implement key transparency at Messenger’s scale, Meta adopted the Auditable Key Directory (AKD) library, the same system used in WhatsApp. This system organizes users’ public keys into a verifiable structure, allowing efficient lookup and proof generation even as key volumes grow. Notably, Messenger handles a significantly higher volume of key changes due to its support for multiple devices per user, each with independent keys that update frequently. Meta reports key publication epochs occur roughly every two minutes, with hundreds of thousands of new key entries per epoch, and billions already logged.
To keep the system both secure and verifiable, Meta has partnered with Cloudflare, which runs an independent auditor for the key transparency logs. This auditor maintains a live dashboard that allows the public to view the current state of the Messenger and WhatsApp key directories, ensuring accountability and transparency in how public keys are distributed.
On the engineering side, Meta introduced several optimizations to improve the efficiency and resilience of the system. These include reducing proof sizes in key verification, making the transparency tree more manageable, and enhancing fault tolerance for key sequencing operations, lessons learned from the two years of operating WhatsApp’s similar infrastructure.
With the rollout of key transparency, Messenger joins a small but growing list of platforms that offer both end-to-end encryption and cryptographic verifiability at a global scale.







Leave a Reply