
The Sysdig Threat Research Team (TRT) reports a sharp increase in LLMjacking incidents, where attackers illicitly access large language models (LLMs) through compromised cloud credentials. This trend reflects a growing black market for access to LLMs, driven by attackers' motives ranging from personal use to circumventing bans and sanctions. The rising frequency and sophistication of LLMjacking have led to significant financial and security risks for cloud users.
Initially, LLMjacking involved unauthorized use of pre-activated models in compromised accounts. However, Sysdig’s latest findings reveal that attackers are now actively enabling LLMs using stolen cloud credentials. This shift has raised the potential daily cost to victims, with some attacks costing over $100,000 per day when using cutting-edge models like Claude 3 Opus. The volume of these attacks spiked in July 2024, with over 85,000 Bedrock API requests recorded on July 11 alone, demonstrating how quickly attackers can deplete resources.
What is LLMjacking?
LLMjacking, a term coined by Sysdig TRT, refers to the illegal acquisition of access to LLMs via compromised cloud credentials. Attackers typically infiltrate cloud environments to locate and exploit enterprise LLMs, passing the operational costs onto the victim. The rise in LLMjacking reflects both the increasing popularity of LLMs and attackers’ growing expertise in exploiting them, especially in cloud-hosted environments like AWS Bedrock.
Attack volume and methods
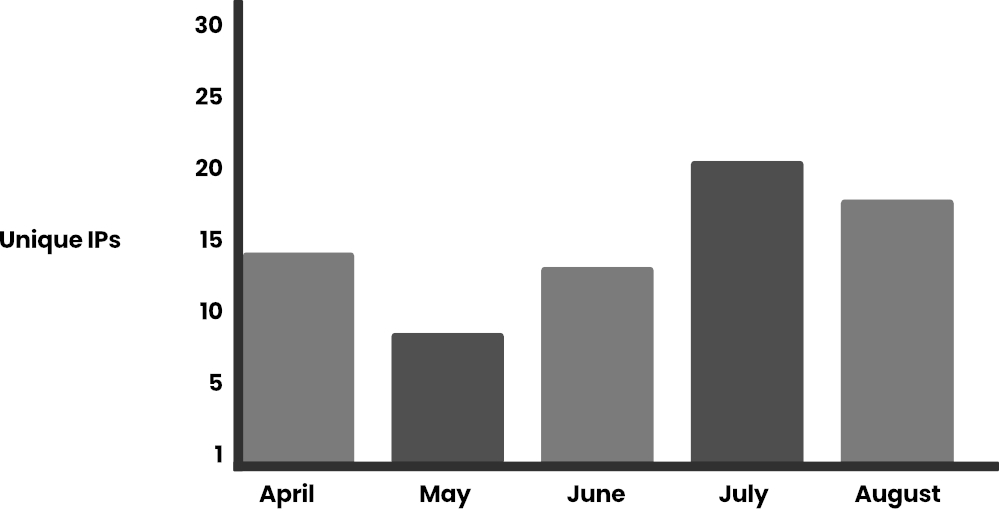
Sysdig TRT tracked the surge in LLMjacking throughout the first half of 2024, noting a 10x increase in LLM requests by July. Attackers primarily used the Bedrock API, with 99% of requests aimed at generating prompts — most of them for role-playing interactions.
The majority of these prompts were in English, followed by Korean and other languages such as Russian and German. Notably, many attacks stemmed from entities in sanctioned countries, like Russia, where access to LLMs has been restricted by major tech companies. Attackers are drawn to cloud-based LLMs to bypass restrictions.
One example involved a Russian attacker using stolen AWS credentials to access Claude models for educational projects, showcasing how attackers can exploit LLMs for a variety of purposes, even in legitimate-seeming contexts.
Evolving techniques and API exploits
LLM-enabled attacks have grown more sophisticated, with attackers leveraging various APIs to evade detection. Sysdig observed increased use of AWS’s newly introduced Converse API, designed for stateful interactions, which allowed attackers to bypass traditional logging systems like CloudTrail.
Additionally, attackers employed advanced scripts to optimize resource consumption by continuously interacting with LLMs and generating content. These scripts demonstrate the evolving nature of LLMjacking, as attackers adapt and refine their techniques.
Another concerning development involves attackers enabling disabled LLM models by exploiting APIs like PutFoundationModelEntitlement. In one observed case, attackers used this API to re-enable a model on AWS Bedrock, suggesting that current cloud security measures may not be enough to prevent unauthorized model activation.
To mitigate the risks associated with LLMjacking, cloud users can take the following steps:
- Strengthen credential protection and enforce strict access controls based on the principle of least privilege.
- Regularly audit cloud environments using frameworks like AWS Foundational Security Best Practices to detect misconfigurations.
- Monitor cloud activity for unusual patterns, particularly around LLM usage, which could indicate compromised credentials or malicious behavior.







Leave a Reply