
Google has issued a security update for Chrome's Stable channel, addressing a high-severity vulnerability in Chrome's Loader component that has been actively exploited in the wild.
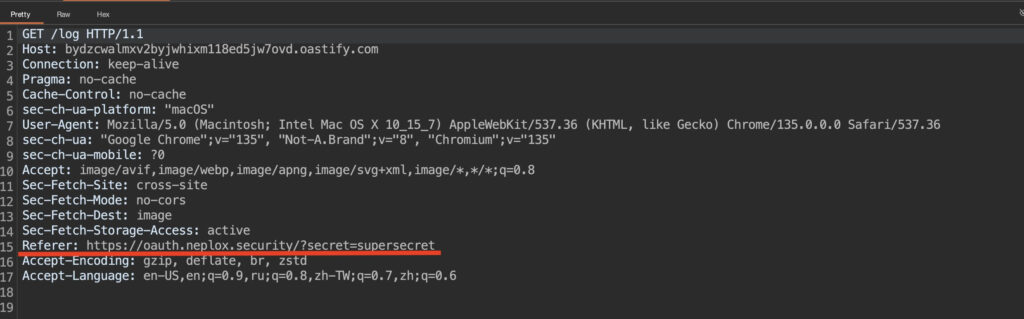
The flaw, tracked under CVE-2025-4664, was publicly disclosed by security researcher ‘@slonser_‘ on May 5, 2025, through a series of technical posts on X. The exploit technique, which was not previously well-known in the security community, abuses Chrome's behavior of resolving Link headers in subresource requests. Specifically, the flaw arises from Chrome's failure to enforce referrer-policy restrictions when handling third-party resources, allowing attackers to extract sensitive data embedded in query parameters.
The bug enables a remote attacker to perform cross-origin data leakage by crafting an HTML page that abuses the Link header to set a permissive referrer-policy, such as unsafe-url. When Chrome loads a subresource like an image from a third-party domain, the referrer — including full query strings — may be sent along, leaking OAuth tokens or other sensitive data embedded in URLs. This opens the door to account takeover scenarios if an attacker can trick a user into visiting a malicious page during a vulnerable authentication flow.
Slonser
Google formally identified and patched the issue in Chrome version 136.0.7103.113/.114 for Windows and macOS, and version 136.0.7103.113 for Linux, released on May 14, 2025. The company acknowledged the existence of public exploits that increase the likelihood of malicious in-the-wild exploitation, increasing the urgency of applying the fix.
The vulnerability was rooted in Chrome's Loader component, which plays a key role in managing subresource requests. This flaw is particularly dangerous because it undermines browser-enforced isolation between websites, a cornerstone of modern web security.
In addition to CVE-2025-4664, the update includes three other security fixes, notably CVE-2025-4609, an unspecified issue in Mojo — a core IPC (inter-process communication) library in Chromium — reported by researcher “Micky” on April 22, 2025. While technical details for that flaw remain undisclosed, it has also been rated as high severity.
It is recommended that Chrome users update their browser as soon as possible through Menu > Settings > About Chrome, and click ‘Relaunch‘ once the download is finished.
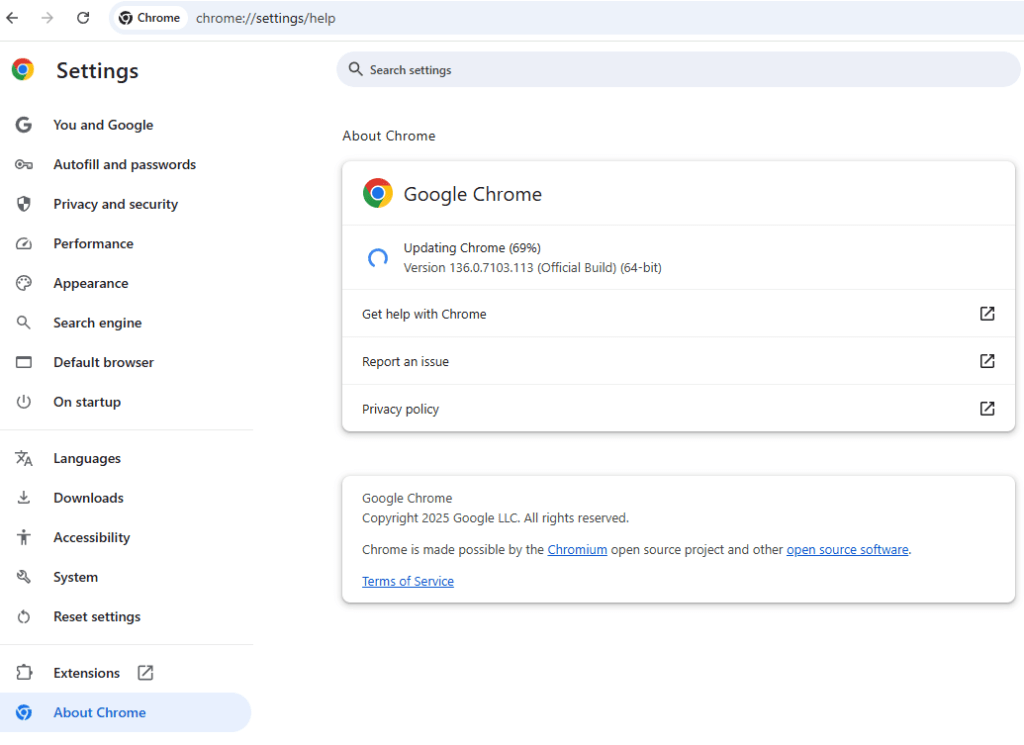
Although the particular flaw hasn't been confirmed as exploited by malicious threat groups, the existence of a public exploit increases the risk significantly, so immediate action to secure Chrome is recommended.







Leave a Reply