
Cisco Talos has unearthed a series of vulnerabilities in certain TP-Link routers, with one particularly alarming flaw capable of reverting the device settings to factory defaults.
Cisco's findings, published yesterday, emphasize the fragility of our network infrastructure, spotlighting the TP-Link AC1350 router as a key example of these vulnerabilities.
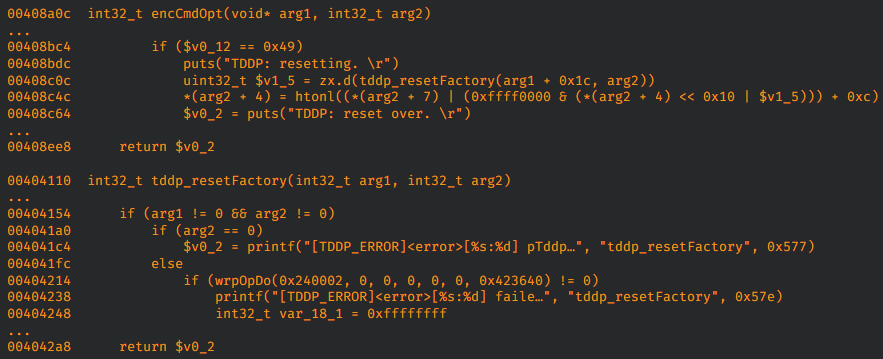
The TP-Link AC1350, a device primarily designed for home networks, has been identified to possess four distinct vulnerabilities. The most critical, TALOS-2023-1861 (CVE-2023-49074), pertains to a denial-of-service (DoS) weakness within the TP-Link Device Debug Protocol (TDDP).
Exploiting this flaw by attackers through a sequence of unauthenticated packets could lead to a DoS condition, forcibly resetting the router to its original factory settings. Interestingly, this vulnerability window is open for approximately 15 minutes following a device's reboot, highlighting a critical time frame where the device's defenses are most vulnerable.
Cisco Talos
Further examination revealed additional vulnerabilities within the TDDP protocol, identified as TALOS-2023-1862 (CVE-2023-49134 and CVE-2023-49133), which enable command execution. These flaws could potentially allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code on the targeted router.
Another concerning vulnerability is encapsulated under TALOS-2023-1888, which involves a cluster of CVEs (CVE-2023-49912, CVE-2023-49909, through CVE-2023-49911). This particular issue allows for remote code execution if an attacker sends an authenticated HTTP request to the router, exploiting multiple buffer overflows to trigger the vulnerability.
Lastly, TALOS-2023-1864 (CVE-2023-48724) impacts the router's web interface, where an unauthenticated HTTP request could cause a denial of service.
For users and network administrators looking to protect against these vulnerabilities, Talos recommends updating to the latest firmware versions provided by TP-Link and adhering to best security practices.
TP-Link released firmware updates to address the above issues on April 3, 2024, which users can download from the vendor's official downloads center (V3 and V4). Alternatively, you can use your device's built-in firmware upgrade mechanism, which is accessible from the admin console.
Implementing network segmentation, regularly updating and monitoring network devices, and downloading the latest rule sets for Snort, an open-source network intrusion detection system, can offer layers of defense against potential exploits. Further details and mitigation strategies are available through Talos Intelligence's advisories and on their website.







Leave a Reply