
A new study reveals critical vulnerabilities in popular mobile instant messengers, including WhatsApp and Signal, that expose users to privacy violations and resource depletion attacks.
WhatsApp and Signal are used worldwide for personal and professional communications. WhatsApp, with over two billion users, has integrated E2EE since 2016, significantly improving privacy. Signal, often favored for its robust security features, underpins encryption protocols in WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger. However, the vulnerabilities identified could undermine trust in these services, especially among privacy-conscious users.
Discovery and key findings
The research was conducted by a team led by Gabriel K. Gegenhuber from the University of Vienna, with collaborators from Intigriti and SBA Research.
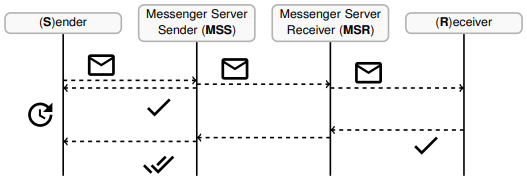
Their work identified how delivery receipts — notifications confirming message delivery — can be exploited to extract sensitive information about a user’s device and behavior. The team discovered that these leaks occur even without an ongoing conversation or user awareness, impacting over two billion users globally.
Arxiv.org
The study’s main findings are summarized as follows:
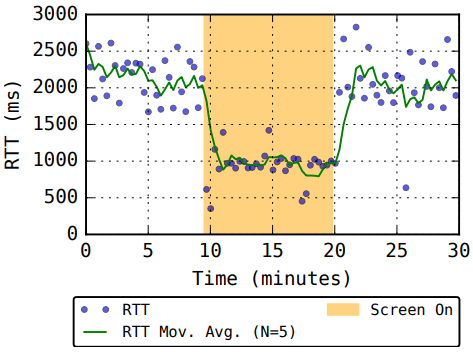
Unintended Data Exposure: Delivery receipts can reveal the number of devices a user has, their operating systems, and their activity states (e.g., screen on/off). Adversaries can monitor app usage or infer behavioral patterns like sleep schedules or location shifts.
Arxiv.org
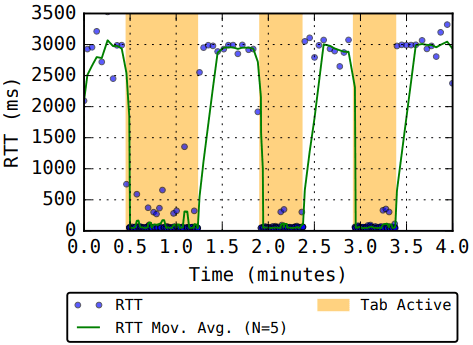
Stealthy Tracking: Attackers, labeled as “spooky strangers” or “creepy companions,” can use reactions to non-existent messages to trigger receipts without notifying the victim. These mechanisms allow covert monitoring, even by individuals who are not in the user’s contact list.
Arxiv.org
Resource Exhaustion: Attackers can exploit these features for denial-of-service attacks by draining a victim’s battery or data allowance. For instance, using WhatsApp, an attacker could inflate data usage to 13.3 GB/hour, depleting battery levels at alarming rates.
Platform Vulnerabilities: While WhatsApp and Signal were heavily impacted, Threema’s architecture provided more resistance, limiting stealthy probes and multi-device leaks.
Defense strategies
The researchers propose several countermeasures:
- Strengthen client-side checks to reject invalid or irrelevant messages.
- Restrict message frequencies to mitigate resource exhaustion attacks.
- Allow users to disable delivery receipts entirely for better privacy.
- Implement synchronized multi-device receipt issuance to reduce leakage.
- Add artificial delays to acknowledgment timings to counteract tracking.
This study underscores the need for a careful balance between usability and security in encrypted messaging platforms. Developers must refine delivery receipt mechanisms and integrate privacy-by-default principles to safeguard user data against emerging threats. Users cannot do much to mitigate the risks other than to remain vigilant and utilize available privacy settings to minimize risks.






Leave a Reply