Did you know that your email messages can be intercepted and read by unauthorized parties? This is possible because not all email services encrypt your messages before sending them out onto the public internet. To prevent this kind or unauthorized access, you should use an encryption tool or an encrypted email service.
In this guide, we’ll explore various encryption protocols and provide step-by-step guides to encrypt emails with some popular services. Get ready to lock down your inbox!
How email encryption works
Essentially, encryption converts regular readable text (plaintext) into encrypted text (ciphertext). To do this, the encryption algorithm creates an encryption key. Likewise, the decryption algorithm that turns ciphertext back into plaintext will provide a decryption key. So, the whole process looks like this:
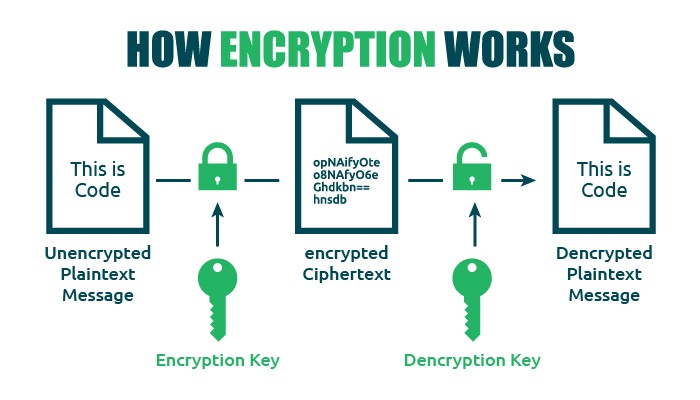
When you encrypt an email message, the body of the message becomes unreadable to anyone but the intended recipient. But what about the rest of the message, such as the subject line or attachments? Some tools and services also encrypt additional content, potentially including the subject line and attachments.
However, certain parts of the email need to remain unencrypted. For example, the email address of the recipient, because that would stop the message from actually arriving at its destination!
Note: Digital signatures come into play as well, adding another layer of security by authenticating the sender’s identity.
What is E2E encryption and why should I use it?
E2E is shorthand for end-to-end. In the context of email E2E encryption (also known as E2EE) means that you encrypt something on your computer or mobile device (one end), and the recipient decrypts it on their computer or mobile device (the other end). Why is this important?
Think about how an email message gets from you to the recipient. First, you type a message and hit Send. This email then passes out of your computer onto a connection controlled by your Internet Service Provider (ISP).
The message then goes to your email provider, who passes it along to another connection controlled by some other service, and so on. Eventually, the message arrives in the recipient’s inbox.
In short, that’s an awful lot of steps. At any one of those, it is possible for someone to try and read your messages. E2E encryption solves this problem. Done right, no one will be able to read your emails except the recipient.
Types of encryption algorithms
There is one more aspect of how encryption works that you need to know about before we can move forward.
Remember, we said turning your message into ciphertext requires an encryption key, and turning it back into plaintext requires a decryption key. This process can be done in one of two ways:
1. Symmetric key encryption
In symmetric-key encryption, the encryption key and the decryption key are identical or closely related. In effect, they are a secret shared between the sender and the recipient.
To send a message using symmetric key encryption, the sender encrypts the message using their copy of the secret key and the recipient decrypts it using their copy of the secret key.
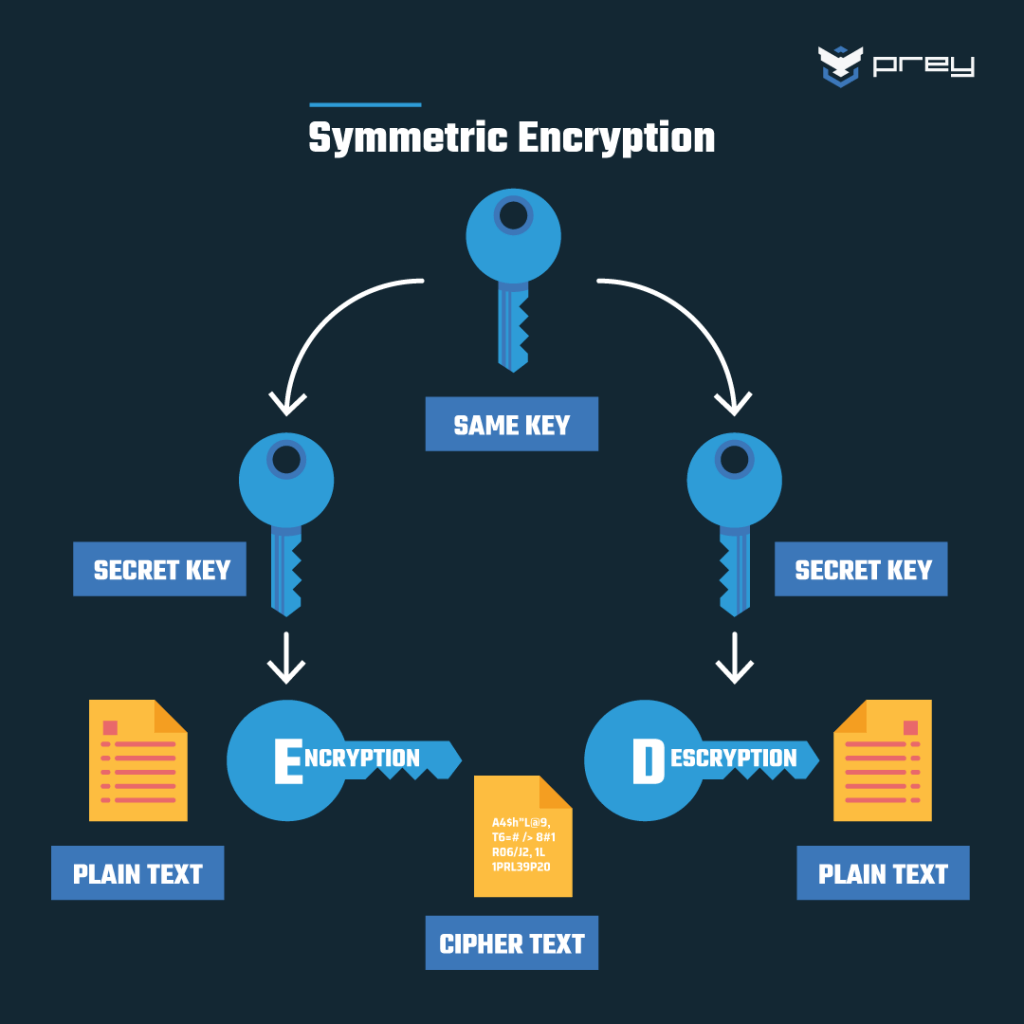
Currently, the most popular type of symmetric encryption is PGP. We will talk about it a bit later. For now, let's turn to…
2. Asymmetric key encryption
In asymmetric-key encryption (public-key encryption) the relationship between the encryption and decryption keys is much more complex. Each person has both a public key and a private key.
The public keys can be shared publicly and are used to convert plaintext to ciphertext. The private keys are kept secret and used to convert ciphertext back into plaintext.
With asymmetric-key encryption, there is no need for a shared secret. Both parties publish their own public keys and keep secret their own private keys.
To send a message using asymmetric key encryption, the sender encrypts the message using the recipient’s public key and the recipient decrypts it using the recipient’s private key.
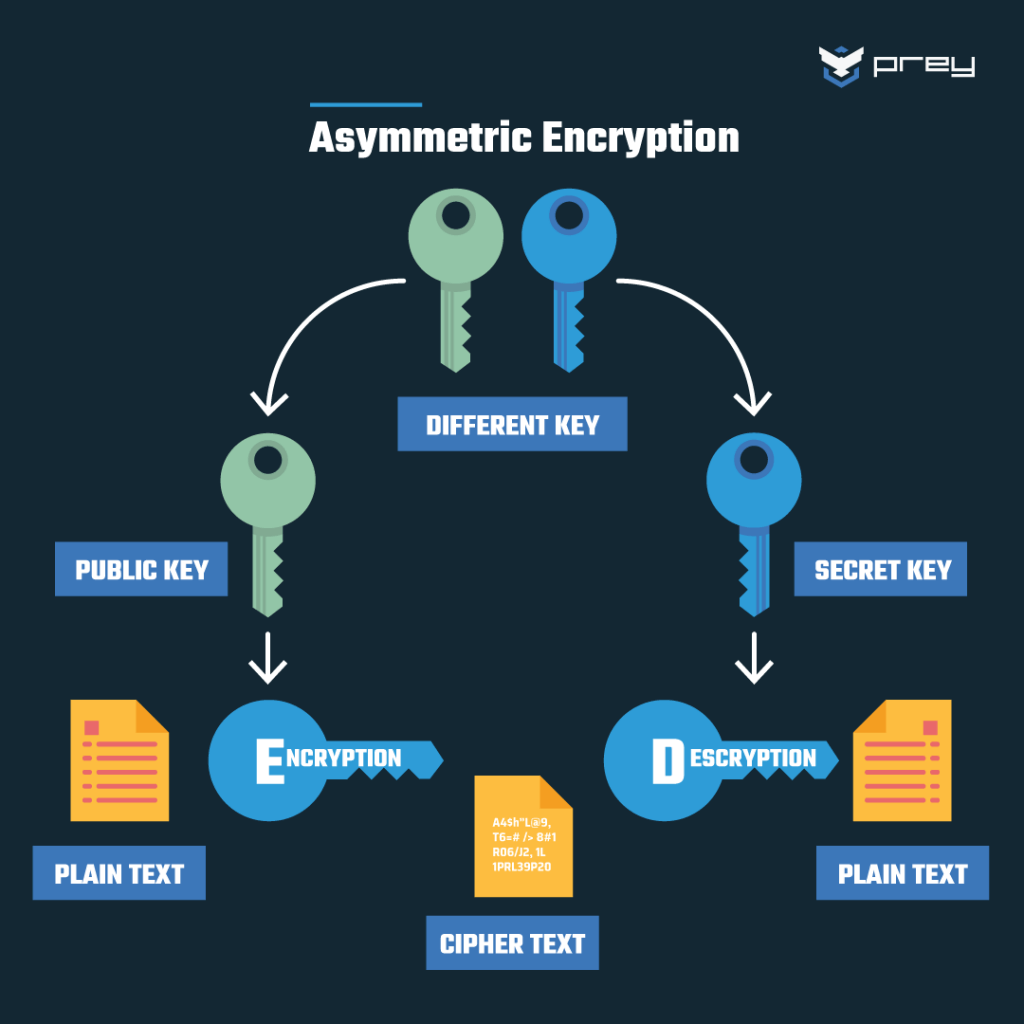
S/MIME and RSA protocols are perfect examples of asymmetric encryption. RSA is used by Tutanota, a secure email service that we've recently reviewed.
Note: There are some protocols, like TLS, that use both types of encryption algorithms.
Pros & cons of encryption algorithms
As you might expect, each approach has positives and negatives.
Symmetric-key encryption is easier to implement and generally can encrypt/decrypt messages faster. However, it requires the sender and receiver to somehow agree on an encryption key and share it through a secure channel. This could require a phone call, face-to-face meeting, or some other creative methods.
Asymmetric-key encryption is more complicated, in that it needs a system in place for discovering the public key of a person you want to communicate with.
This is handled by Certificate Authorities, who issue digital certificates that confirm who is an owner of a particular public key. For this to work, Certificate Authorities need to be trusted services. The upside is that they make it possible to send encrypted messages to someone you have never communicated with before.
Types of encryption protocols
S/MIME and PGP/MIME are two primary email encryption protocols in the digital realm. Think of them as Batman and Superman, each with their unique powers and abilities.
S/MIME encryption relies on certificates to verify the security of messages. Imagine it as a digital stamp of approval, ensuring the recipient that the message is safe and sound.
On the other hand, PGP/MIME uses the recipient’s private and public encryption keys. It is faster, but also not as secure as S/MIME.
Risks and limitations of email encryption
Despite the numerous benefits of email encryption, it's crucial to be aware of its potential downfalls. For instance, there have been documented security vulnerabilities in both PGP and S/MIME protocols.
Other limitations of email encryption include:
- Compatibility issues — Email providers use different types of encryptions. For example, if you use Proton Mail (PGP) and your recipient has Tutanota (AES and RSA encryption), you won't be able to send encrypted emails to each other. These days, it seems better to subscribe to a provider that uses PGP, since it is so prevalent.
- Key management — If you lose your private encryption key you can easily lose access to all of your encrypted emails. Your keys may also get compromised, meaning that a hacker could get access to all of your sensitive messages.
- Regulatory challenges — Depending on your jurisdiction, there may be laws in place forcing email services to disclose emails/encryption keys. This is a major problem in the US. Its best to look for European-based encrypted email providers based in countries that respect user privacy, such as Germany and the Netherlands.
Inconvenient — Encrypting emails requires additional steps, like exchanging public keys or managing certificates. Since this process is not as user-friendly as just hitting a send button, many users won't rely on it. Also, your recipient has to be familiar with decryption, otherwise, he will be unable to access your messages.
- Shady email providers — Certain services don't use full E2E encryption, meaning that your messages can be accessed when stored at rest on your provider's servers. This is why it is important to choose a trusted service, like Proton Mail.
Despite these challenges, using email encryption is still an essential component of secure online communication. Staying informed about potential risks and limitations will help you in making informed decisions.
How to encrypt email
There are two ways in which you can encrypt an email: using third party tools or switching to a secure email provider.
On the assumption that you are not prepared to change email services right now, we are first going to talk about how you can use E2E on a service like Gmail to encrypt the bodies of your messages.
Note: While it requires a bit more work, switching to a secure email provider with built-in E2E encryption is a better way to go.
How to encrypt emails in Gmail
Despite its security problems, Gmail supports E2E encryption. To set it up, we will have to use one third-party service. Here are some candidates.
1. FlowCrypt
FlowCrypt integrates seamlessly with Gmail and is available as a free extension. It indicates encryption levels by color codes, so you can quickly identify the security status of your messages. It goes from green (S/MIME) to gray (TLS) to red (no encryption).
2. Mailvelope
Alternatively, you can also try Mailvelope. This is a popular browser extension that uses the OpenPGP protocol. It is available on Chrome, Firefox, and Edge and works perfectly with Gmail and other popular email services.
3. GPGTools
GPGTools uses GPG (GNU Privacy Guard) keys to encrypt emails and files. GPG is an open-source version of PGP, so you can expect a similar level of security
Encrypting emails in Outlook
Note: Setting up encryption in Outlook requires a digital certificate or ID. You can get them from your organization’s administrator.
Thanks to S/MIME support, Outlook users can also benefit from email encryption. Once you have the certificate, you’re ready to send and receive encrypted emails. Just remember that both parties need to have each other’s digital signatures and certificates saved in their respective keychains (address books) to make the magic happen.
Securing emails on iOS
S/MIME encryption is also available on Apple devices, so you won't have to use external apps. To enable it, visit Settings > Mail > Accounts and select to which users you want to send encrypted emails by default.
Note: Always keep an eye out for lock icons next to recipients’ email addresses. A red lock icon indicates that you cannot send encrypted messages, while a blue lock icon means you’re good to go.
Android Email Encryption
Android users will have to get a third-party app like CipherMail and OpenKeychain to get E2EE. Both of these apps support S/MIME and PGP/MIME, while CipherMail also offers TLS and PDF encryption.
By integrating these apps with your email client, you can ensure that your messages are well-protected from outsiders
Best encrypted email services
Third-party apps are convenient, but it is much better to switch to a secure provider that uses E2EE. There are many to choose from, but not all of them are really secure.
To save you the headache, we'll do a quick overview of our favorites. If you want to go more in-depth or find more alternatives, head on to our article on the best encrypted email services.
1. Proton Mail — Popular Swiss E2E email service
| Based in | Switzerland |
| Storage | 15 – 1,000 GB |
| Price | $3.00/mo. |
| Free Tier | Up to 1 GB |
| Website | Proton.me |
Proton Mail is a popular encrypted email service that offers:
End-to-end PGP encryption for your messages.
Encryption starts from your device, ensuring only the intended recipient can decrypt and read your emails.
Pricing plans based on domains and daily message limits, providing flexible options to fit your needs.
- Strong cross-platform support.
With its robust encryption features, Proton Mail guarantees secure email communication. It is located in Switzerland, which is an excellent jurisdiction when it comes to user privacy. Proton Mail also has an intuitive interface, which makes it a solid option for casual users.
For more details, take a look at our Proton Mail review.
+ Pros
- End-to-end (E2E) and zero-access encryption for Email, Calendar, and Contact information
- Operates under Swiss jurisdiction
- All data stored on servers in Switzerland
- Apps for Android and iOS mobile devices
- Web client, encryption algorithms, Android and iOS code are all open-source
- Support for custom domains
- Strips IP addresses from emails
- Can be used with third-party email clients through the Proton Mail Bridge feature
- Can import contacts and emails
– Cons
- Subject lines not encrypted
- May require personal information for verification of new accounts
Proton Mail Coupon:
Get 40% Off Proton Mail one-year plans using the exclusive coupon below:
(Coupon is applied automatically; 30-day money-back guarantee)
Learn more in our updated Proton Mail review.
2. StartMail — Secure email encryption from the Netherlands
| Based in | The Netherlands |
| Storage | 20-30 GB |
| Price | $2.00/mo. |
| Free Tier | 7-day trial |
| Website | StartMail.com |
StartMail is another service that supports PGP email encryption. It is also compatible with popular email clients like Outlook and Gmail. With it, you can send encrypted messages without worrying about compatibility issues or going through a complex setup.
StartMail offers a variety of security features, including:
- E2E PGP encryption
Immediate encryption of incoming emails
- Temporary disposable Email Aliases
With StartMail, you can enjoy secure email communication without sacrificing convenience.
+ Pros
- Create unlimited email aliases
- PGP end-to-end encryption
- Easy contacts and email migration
- Organize your inbox with filters
- Minimalistic design
- No ads. No tracking. No spam.
- Flexible spam filter
- Anonymous cryptocurrency payments
- Use custom domain
- Compliant with GDPR
- 7-day free trial
– Cons
- No free version
- Lacks calendar, notes, and file storage
StartMail Exclusive Coupon:
Get 60% off ANY subscription plan with the coupon below along with a 7-day free trial:
(Enter INSIDER60 coupon code at checkout)
Our StartMail review has more information on this quality service.
3. Mailfence — Affordable email encryption
| Based in | Belgium |
| Storage | 11 – 225 GB |
| Price | 2.75/mo. |
| Free Tier | Up to 1 GB |
| Website | Mailfence.com |
Mailfence is an encrypted email service that uses OpenPGP E2E encryption, digital signatures, and secure storage for your messages. There are also additional tools, like calendar, groups, and file storage.
Mailfence's encryption system is intuitive and easily managed even if you are not familiar with PGP encryption. With its strong focus on privacy and security, Mailfence is an excellent choice for users seeking an affordable encrypted email.
Our Mailfence review will tell you everything you need to know about this service.
Additional security measures
Encrypting emails is just the first step in securing your online communication. Additionally, you should use strong passwords for your email accounts. For safety and convenience, consider storing them in a password manager.
Another crucial security measure you should enable is two-factor authentication (2FA). This adds an extra layer by requiring two forms of identification.
If possible, avoid using public Wi-Fi networks for sending sensitive information. These networks have many weak points that can be used by hackers to extract your data.
Finally, be wary of phishing emails, which are designed to trick you into revealing personal information or clicking on malicious links.
By implementing these security practices, you can ensure that your email messages remain safe.
Advanced email topics
While you now have the information you need to handle current email encryption, there are some advances that will be affecting encryption and email services in the near future. Topics to keep alert for include:
- Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) — Quantum computers are coming, and it is believed that they will one day be able to defeat (crack) current encryption algorithms. There are even rumors of hostile forces capturing encrypted messages now, with the goal of decrypting them in the future when the technology is available. VPN services are beginning to implement PQC options, and email services like Proton Mail have started working on it too. Without guidance on migrating to PQC-enabled tools (e.g., Proton Mail's partial support or OpenPGP updates), users risk future-proofing failures. Recommend checking services' PQC roadmaps.
- Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) — In PFS, session keys are ephemeral to prevent past messages from being decrypted if a long-term key is compromised. Some email encryption protocols support this feature but not all. If this is important to you, check the specs for any encrypted email service you are considering.
Final words on email encryption
Email encryption is a vital component of secure online communication. By understanding various protocols on the market, you can effectively protect your sensitive information. Remember to enhance your email security with extra measures like strong passwords and two-factor authentication. Stay vigilant with encrypting your important emails, and your data will remain safe.
And also check out our guide on the best encrypted email services for more info.


Leave a Reply