
A CitizenLab report provides the first public analysis of WeChat's MMTLS encryption protocol, revealing several cryptographic weaknesses.
Despite improvements over earlier versions, the encryption used by the app, which has over a billion monthly active users, lacks modern security features like forward secrecy and relies on a custom encryption approach that may expose user data to risks.
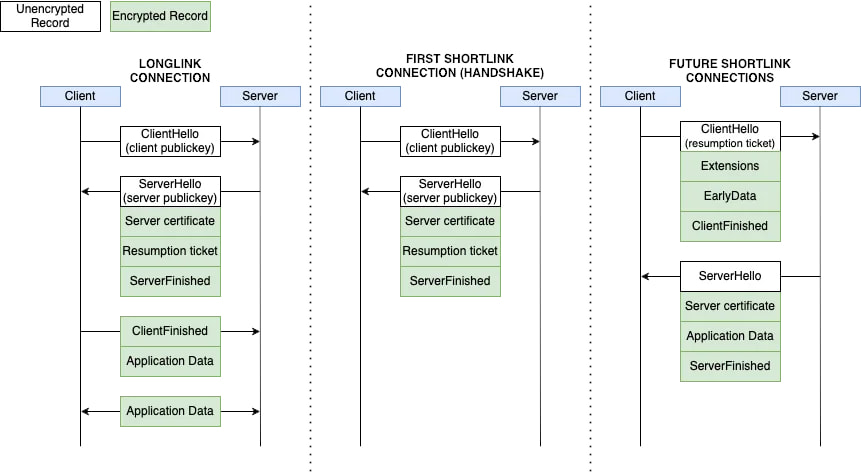
WeChat's MMTLS is a modified version of TLS 1.3, but changes introduced by WeChat's developers, such as the use of deterministic initialization vectors (IVs), weaken the protocol's security. The research shows that WeChat continues to employ a legacy layer of encryption, termed “Business-layer encryption,” in tandem with MMTLS.
This older system was found to contain vulnerabilities, raising concerns about the app's ability to protect user data. While the researchers could not break WeChat's encryption completely, they noted that the app's cryptography falls short of the standards expected for an app of its scale.
WeChat, owned by Tencent, is the leading messaging platform in China, with over 1.2 billion users globally. Its wide range of features extends far beyond messaging, including social media, payments, and third-party integrations, making it an essential app for many users. Despite its critical role, the platform's proprietary encryption has not been subject to the same rigorous testing as standard protocols like TLS, which are widely used and studied for security.
The researchers examined WeChat versions 8.0.23 and 8.0.21 on Android, employing tools like Frida, Jadx, Ghidra, and Wireshark to analyze the network traffic and app behavior. They identified significant issues with how MMTLS handles key generation, session resumption, and encryption, pointing out that WeChat's reliance on pre-shared keys and long-lived connections makes it vulnerable to attacks where older, compromised keys can be used to decrypt future communications.
CitizenLab
Tencent has acknowledged some of these weaknesses and stated they are transitioning from AES-CBC to the more secure AES-GCM for Business-layer encryption. However, as the researchers point out, the widespread use of MMTLS in WeChat means the protocol will continue to require scrutiny from the security community.
For users, particularly those concerned about privacy, it is recommended to:
- Avoid using WeChat for sensitive communications.
- Ensure the app is updated regularly to receive any security improvements.
- Limit the use of Mini Programs and embedded services, which may expose additional data.
Developers, especially those creating apps for large user bases, are urged to avoid custom cryptographic protocols and adopt well-established encryption standards such as TLS or QUIC.







Leave a Reply