Researchers at Avast have uncovered a significant vulnerability in the cryptographic schema of the DoNex ransomware and its earlier versions. This discovery has enabled them to provide a decryptor to victims of the ransomware since March 2024, a service that was conducted quietly in cooperation with law enforcement until it was disclosed at Recon 2024.
Ransomware evolution
The DoNex ransomware, initially appearing as Muse in April 2022, has undergone several rebranding phases:
- April 2022: Muse
- November 2022: Fake LockBit 3.0
- May 2023: DarkRace
- March 2024: DoNex
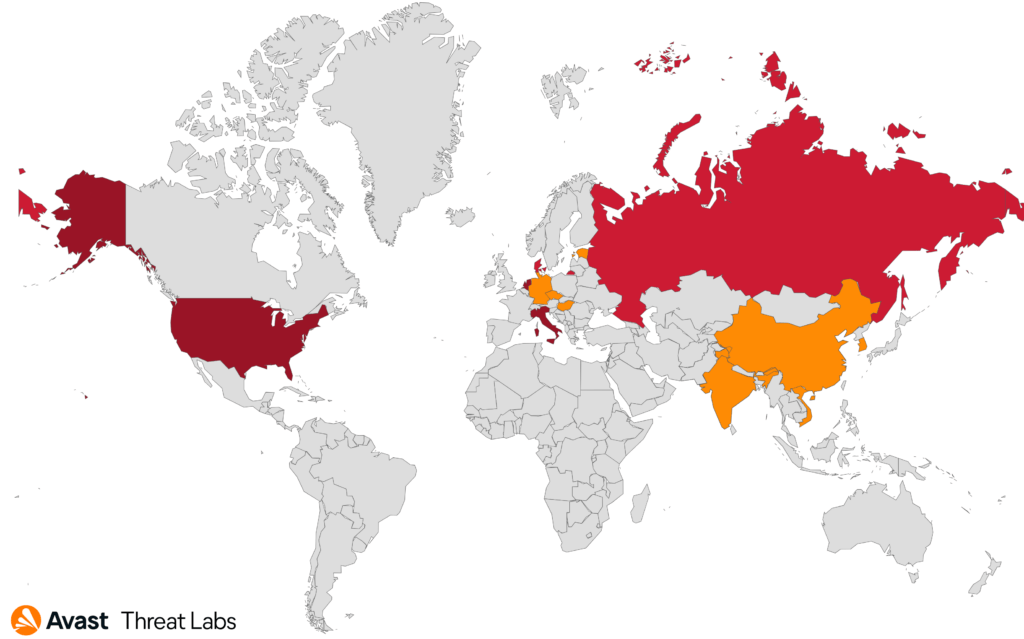
Avast's telemetry data indicates that DoNex has ceased its activity since April 2024, with no new samples detected and the ransomware's TOR site becoming inaccessible. This cessation suggests that the operators might have halted their operations or moved to different platforms.
Avast
DoNex ransomware employs a sophisticated encryption methodology designed to maximize disruption while maintaining system stability. During its execution, an encryption key is generated via the CryptGenRandom() function, which initializes a ChaCha20 symmetric key used for file encryption.
This symmetric key is subsequently encrypted with RSA-4096 and appended to the end of the encrypted file. The ransomware targets files based on their extensions, as specified in an XML configuration file. Files up to 1 MB are fully encrypted, while larger files undergo intermittent encryption, where the file is split into blocks, and those blocks are encrypted separately.
The configuration file includes several lists to refine the encryption process. Allowlisted extensions denote file types that are exempt from encryption, ensuring critical system operations remain unaffected. Similarly, allowlisted files are specific system files that the ransomware avoids encrypting, and whitelisted folders are crucial directories left untouched to ensure the system remains operational.
To enhance the impact of encryption, DoNex terminates specific processes, such as SQL and Oracle, listed under ‘Services to Kill.' The configuration also specifies blocklisted databases, identifying particular database files to be encrypted. Additionally, the number of parallel encryption threads is set to 30 by default, optimizing the encryption speed and efficiency.
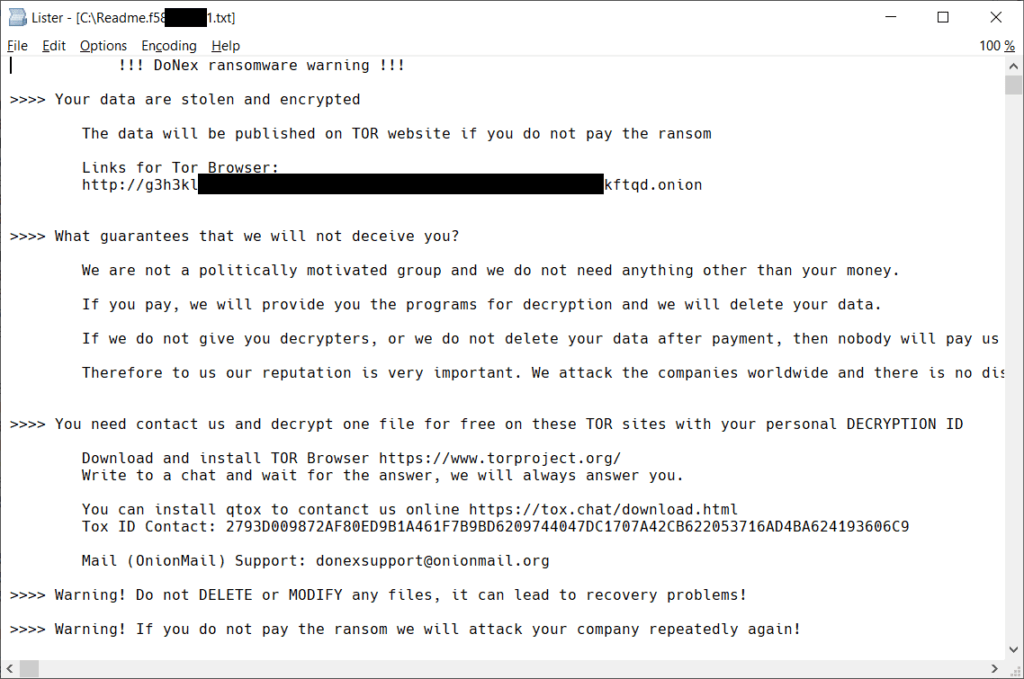
Victims can identify a DoNex ransomware attack through the ransom note left by the malware. Despite different branding, the ransom notes of Muse, Fake LockBit, DarkRace, and DoNex share similar layouts.
Avast
DoNex decryptor
Avast's decryptor, available for download from here, guides users through a simple decryption process involving the following steps:
- Run the decryptor as an administrator.
- Follow the wizard to configure the decryption process, including the license agreement and file location selection.
- Provide an example of an original and encrypted file for decryption. Larger files are preferred for effectiveness.
- The tool will crack the encryption password, a process requiring substantial system memory.
- Back up encrypted files before decryption, which ensures a safety net in case of errors.







Leave a Reply