
In collaboration with Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG), Mandiant has detected a persistent and sophisticated campaign by the cyber threat group APT41.
Targeting various sectors, including global shipping and logistics, media and entertainment, technology, and automotive industries, APT41 has successfully compromised multiple organizations, predominantly in Italy, Spain, Taiwan, Thailand, Turkey, and the United Kingdom.
APT41 is a notorious cyber threat group known for its Chinese state-sponsored espionage activities and financially motivated operations. The group has a history of targeting sectors such as healthcare, high-tech, and telecommunications. The group is known for its sophisticated techniques, including using non-public malware for espionage and financially motivated intrusions into the video game industry.
The victims of their latest campaign span several continents and industries. In the shipping and logistics sector, most targeted entities operate in Europe and the Middle East, often as subsidiaries of larger multinational corporations. In contrast, all affected media and entertainment organizations were based in Asia. Mandiant also observed reconnaissance activities targeting similar organizations in other countries like Singapore, suggesting a potentially broader scope of targeting.
APT41’s latest TTPs
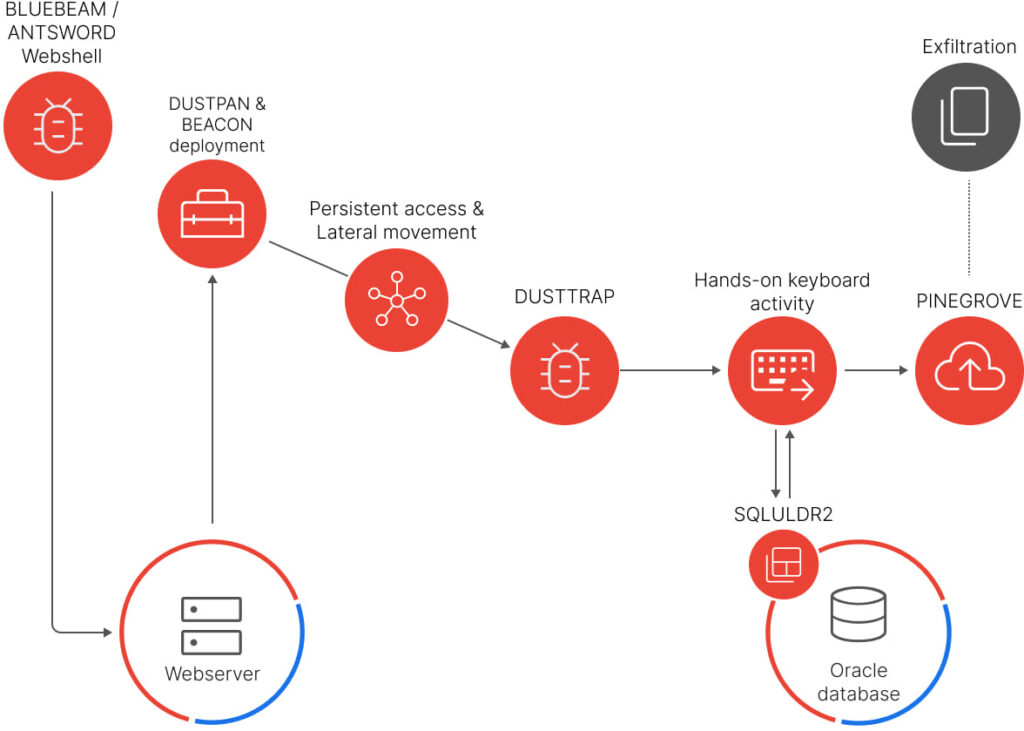
In this campaign, ongoing since 2023, the attackers use a combination of ANTSWORD and BLUEBEAM web shells to deploy the DUSTPAN dropper, which subsequently loaded the BEACON backdoor for command-and-control (C2) communications. The attackers further escalate their operations by deploying the DUSTTRAP dropper to execute more complex tasks. These tools allow APT41 to maintain prolonged, unauthorized access to the compromised networks, enabling extensive data extraction.
Mandiant
APT41’s attack methodology is marked by the following key stages:
- Initial compromise: Web shells (ANTSWORD and BLUEBEAM) were used on Apache Tomcat servers to download the DUSTPAN dropper.
- C2 establishment: DUSTPAN facilitated the stealthy loading of the BEACON payload for ongoing C2 operations.
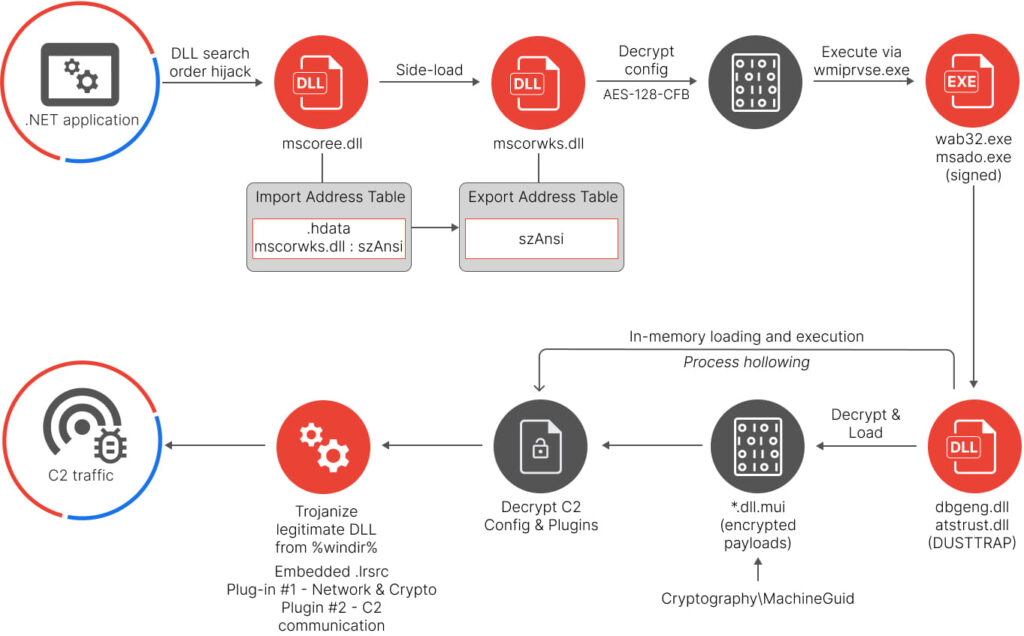
- Advanced intrusion: Deployment of DUSTTRAP, which decrypts and executes malicious payloads in memory, minimizing forensic footprints. This payload is connected to either APT41-controlled infrastructure or compromised Google Workspace accounts.
- Data exfiltration: Tools like SQLULDR2 were used to export data from Oracle databases, and PINEGROVE facilitated data exfiltration to Microsoft OneDrive.
DUSTPAN is an in-memory dropper that decrypts and executes payloads like BEACON, a backdoor that communicates with C2 servers using Cloudflare infrastructure.
DUSTTRAP is a multi-stage framework that decrypts and executes payloads in memory, and it uses advanced evasion techniques to avoid detection. DUSTTRAP plugins perform various malicious operations, from process execution to data exfiltration and system information gathering.
Mandiant
Finally, SQLULDR2 exports data from Oracle databases, while PINEGROVE, a command-line uploader, exfiltrates data to OneDrive using the OneDrive API.
To stop or at least put obstacles along the way of sophisticated threat actors like APT41, Mandiant recommends isolating critical infrastructure through network segmentation, implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) across all accounts, and ensuring that all systems are up-to-date and running on the latest security patches.







Leave a Reply