
McAfee Labs recently uncovered a novel malware delivery method dubbed “Clickfix,” leveraging social engineering tactics to deceive users into executing harmful scripts.
The Clickfix infection chain begins by redirecting users to websites that host deceptive popup windows. These popups instruct users to paste a script into their PowerShell terminal, a move that, once executed, facilitates malware infiltration on the victim's device.
This technique capitalizes on the appearance of authenticity, making it a potent form of social engineering. Once the script is run, it can lead to data theft, system compromise, or further malware propagation.
Key malware families using this technique include Lumma Stealer and DarkGate, both known for stealing sensitive information, providing remote access, establishing persistent backdoors, and employing advanced evasion tactics.
McAfee Labs also intercepted a phishing email with an HTML attachment, masquerading as a Word document, further demonstrating the elaborate ruses employed by these attacks.
DarkGate infection chain
The phishing email contained an HTML file that, when opened, displayed an error prompt designed to trick users into taking actions leading to malware execution.
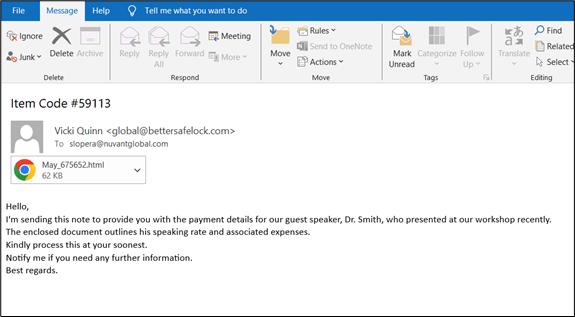
The file suggested the user needed to install a ‘Word Online' extension, providing a button labeled “How to fix.” Analyzing the underlying code revealed base64-encoded content within the HTML's tag.
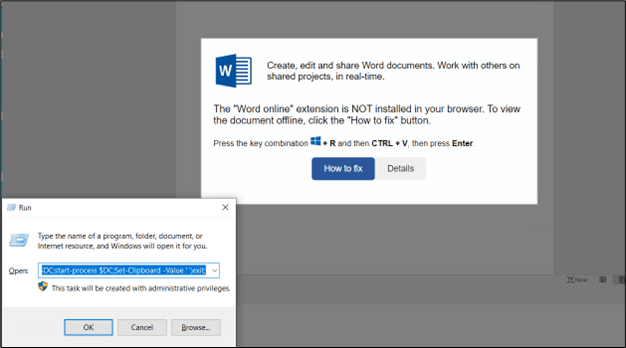
Decoding this content disclosed a PowerShell command intended to download and execute a harmful HTML Application (HTA) file from a specified URL. This HTA file, once executed, initiates malicious actions on the victim's system, including communicating with its command and control (C2) server.
Lumma Stealer infection chain
Similar tactics were observed with Lumma Stealer. McAfee Labs found a website that displayed an error message suggesting browser issues.
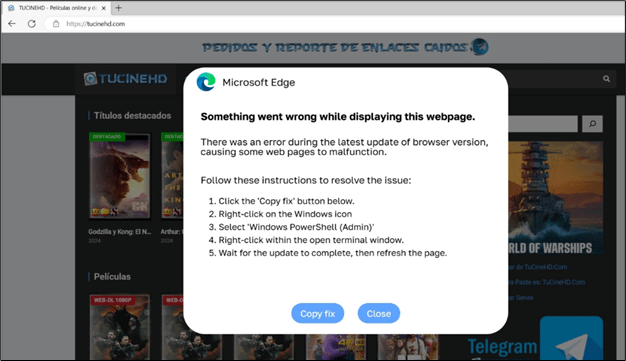
The site instructed users to follow steps that involved copying a script into PowerShell, which, when decoded, revealed commands to download and execute a script from a remote server. This script, once executed, performed malicious activities such as downloading further malware and hiding its tracks by clearing the clipboard.
Users are recommended to treat unsolicited emails with caution and keep their antivirus and OS up to date by applying the latest available security updates. When prompted to perform actions within software tools, test them on virtual machines first, if possible, to verify their safety.







Leave a Reply