Forescout Research's Vedere Labs has uncovered 14 new vulnerabilities affecting DrayTek routers, including both residential and enterprise models. Among these, one vulnerability received a maximum CVSS severity score of 10, while another scored a critical 9.1. These weaknesses could allow attackers to gain control over the routers and infiltrate enterprise networks. Patches have already been released by DrayTek to address these issues.
Severe security risks
The newly discovered vulnerabilities in DrayTek routers vary in impact, including cross-site scripting (XSS), denial-of-service (DoS), and remote code execution (RCE). Some notable ones include:
- FSCT-2024-0006: A buffer overflow in the “GetCGI()” function that could lead to a complete device compromise, rated with a severity score of 10.
- FSCT-2024-0007: An OS command injection in the “recvCmd” binary, allowing VM escape and execution of arbitrary commands, with a score of 9.1.
- FSCT-2024-0001: A shared admin credential issue across guest and host operating systems, allowing full system compromise if credentials are obtained.
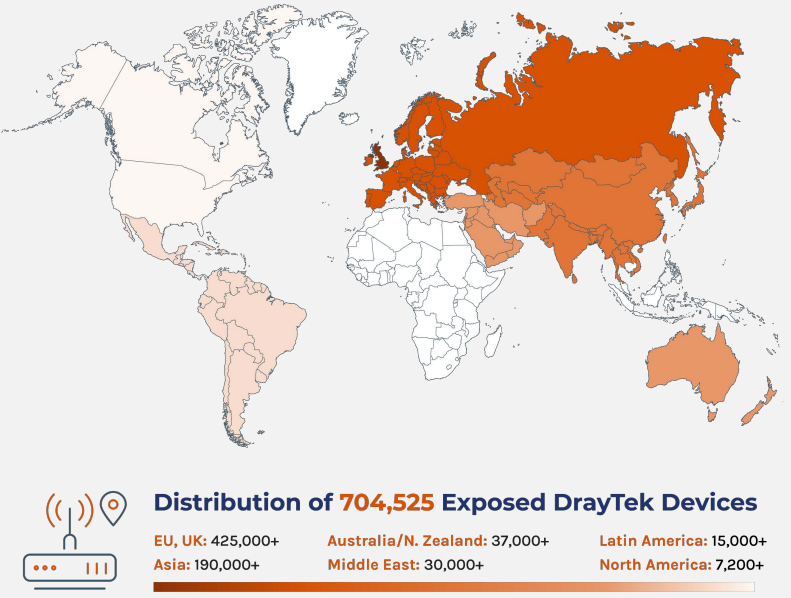
Approximately 785,000 DrayTek routers are operating globally, many of which are accessible over the internet. The exposure is alarming, as around 700,000 devices have their web user interface (Web UI) open to the public network, contrary to the recommendation that it be accessible only from local networks. Nearly 38% of these devices are still vulnerable to similar security issues identified two years ago.
Forescout
DrayTek routers deployment and impact
DrayTek, a networking solutions provider, produces routers for small to medium businesses (SMBs), residential use, and enterprises. The affected routers are widely used across various industry verticals, including healthcare, retail, manufacturing, and finance. Forescout's data analysis, based on its Device Cloud spanning 19 million devices, identified that most exposed DrayTek devices are used in the United States, Spain, Australia, and Israel.
The table below lists some of the affected device models and their respective firmware versions containing the patches:
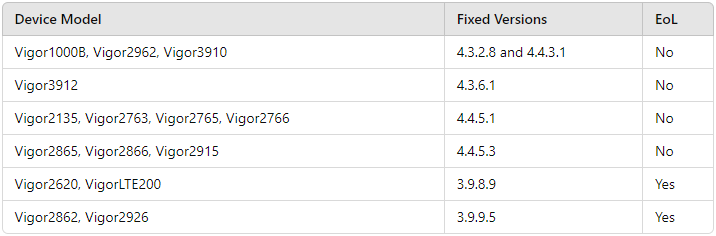
Patching these devices is crucial as some models are end-of-life (EoL), meaning they will not receive ongoing support except for the critical vulnerability FSCT-2024-0006.
Complete protection requires patching all affected devices with the latest firmware provided by DrayTek. Additionally, some key security recommendations include:
- If not necessary, turn off remote access on the router, or if needed, implement an Access Control List (ACL) and two-factor authentication (2FA).
- Regularly verify that no unauthorized remote access profiles or admin users have been added.
- Temporarily disable SSL VPNs until updated firmware is in place, as ACLs might not cover these connections.
- Always back up configurations before updates, and use secure protocols such as HTTPS for network communication.
If you are using any of the EoL models that received an update in this case, consider this your final warning that you have to move to a newer and actively supported router model, as it's all but guaranteed that the vendor will release security updates for future problems.







Leave a Reply