
Researchers identified critical security vulnerabilities in D-Link DSL6740C modems worldwide, posing a significant risk to users. These vulnerabilities allow attackers to bypass authentication, execute arbitrary system commands, and access confidential system files.
Chiao-Lin Yu, also known as Steven Meow, uncovered the vulnerabilities and disclosed three specific security flaws in Taiwan’s CERT page. The findings were published under the identifiers CVE-2024-11068, CVE-2024-11066, and CVE-2024-11067. Each flaw represents a distinct security issue, yet together, they provide a layered attack surface for remote and local attackers.
D-Link modems at risk
Incorrect Use of Privileged APIs (CVE-2024-11068): The D-Link DSL6740C model suffers from a critical misconfiguration in privileged API use, allowing unauthorized remote attackers to modify user passwords without authentication. This opens access to the device’s web interface, SSH, and Telnet services, permitting attackers complete administrative control. CVSS Score: 9.8 (Critical)
OS Command Injection (CVE-2024-11066): Attackers with administrative privileges can execute arbitrary system commands by injecting commands through a vulnerable web page. This vulnerability could allow further compromise of the device and any connected systems. CVSS Score: 7.2 (High)
Arbitrary File Reading through Path Traversal (CVE-2024-11067): A path traversal vulnerability permits unauthorized access to sensitive system files. The device’s default login credentials, generated using the MAC address, can be leveraged to log in once attackers retrieve the MAC address via this vulnerability, granting further unauthorized access. CVSS Score: 7.5 (High)
Impact and risk mitigation
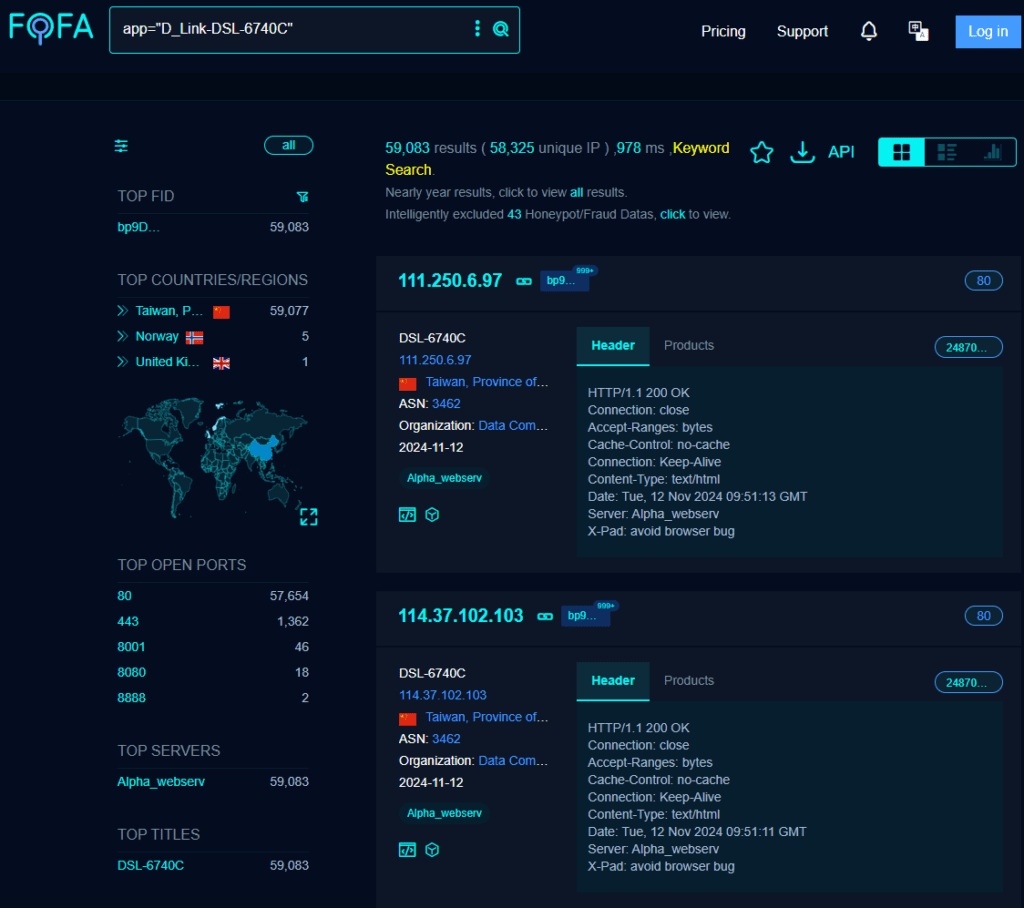
The D-Link DSL6740C is a widely used modem model, with 59,000 exposed units identified via FOFA search results, primarily in home networks and small businesses. These modems are particularly susceptible because they have reached their end-of-life (EoL) phase, meaning D-Link will no longer provide security updates or support for them. As a result, users cannot rely on firmware patches to address these issues, and the device remains vulnerable to potential attacks indefinitely.
CyberInsider
Given the high exposure of these D-Link modems, the vulnerabilities could allow attackers to infiltrate and control connected networks, potentially leading to data theft, network disruptions, and other significant impacts, especially for smaller organizations that may lack dedicated IT security resources. The critical API misuse vulnerability, in particular, elevates the risk by allowing attackers to seize device control remotely without user credentials.
Since D-Link is not expected to release updates or patches for the DSL6740C modem, users should take the following actions immediately:
- Replace the D-Link DSL6740C with a modem model that is currently supported and actively receiving security updates.
- Disabling remote access features such as web, SSH, and Telnet services may reduce the risk.
- Separate vulnerable devices from sensitive or critical networks to minimize potential damage if they are compromised.
- Regularly monitor network traffic for suspicious activity to detect exploitation attempts on exposed devices.







Leave a Reply